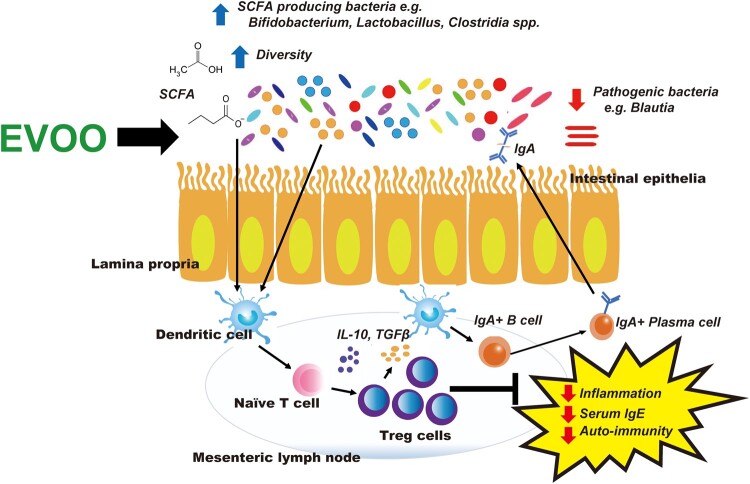
Figure 3.
Impact of extra-virgin olive oil (EVOO) on gut microbiota and mucosal immunity. Extra-virgin olive oil modulates the gut microbiota by acting as both a prebiotic (encouraging the growth of beneficial bacteria) and antibacterial (reducing the growth of pathogenic bacteria). Extra-virgin olive oil promotes the growth of certain bacteria that are capable of producing microbial metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). Short-chain fatty acids and other gut microbiota-generated metabolites can positively influence the mucosal immune system by increasing T-regulatory (Treg) cells as well as the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 and TGF-β, which assist in reducing local inflammation and promoting immune tolerance to commensals and other harmless dietary antigens. Extra-virgin olive oil may also promote an increase in intestinal IgA, providing further protection against pathogenic bacteria and promoting homeostasis of the gut microbiota.