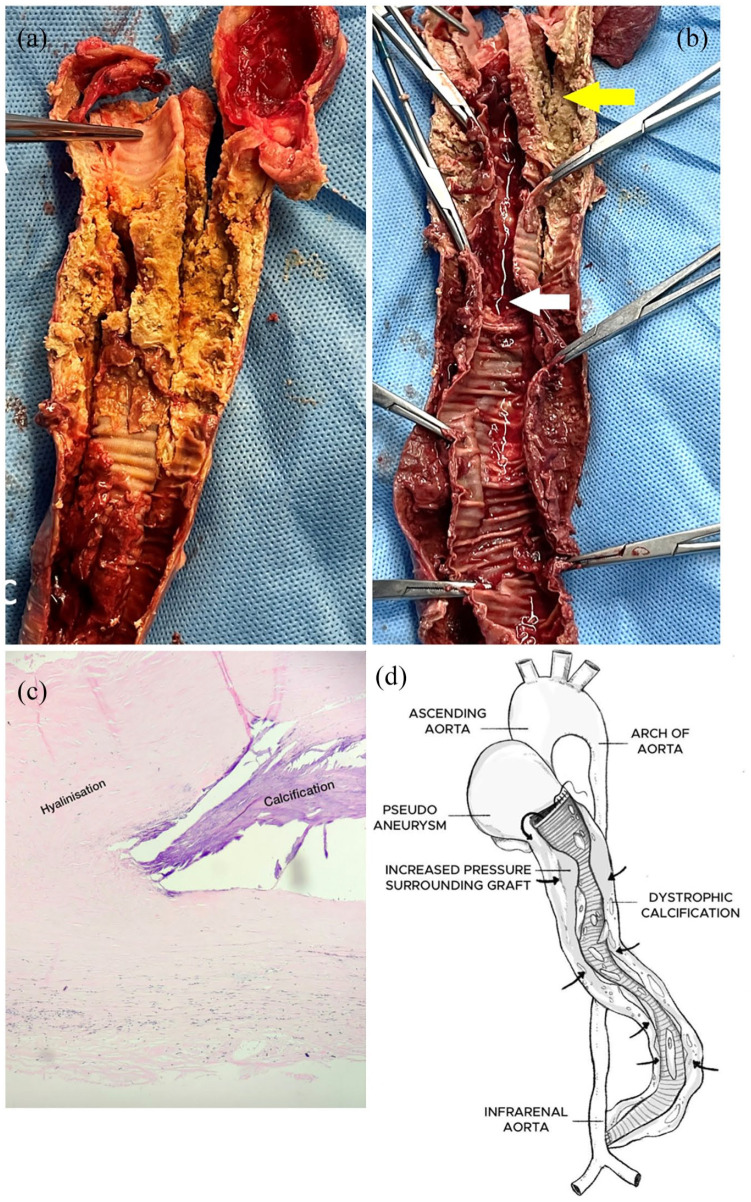
Figure 3.
(a) Cut section of the extra-anatomical graft showing extensive dystrophic calcification and organized thrombus. (b) Inner surface of extra-anatomical graft showing lumen filled with thrombosed blood (white arrow). Outer tubular capsule surrounding graft showing calcification (yellow arrow). (c) Histopathological slide of the tissue surrounding the excised graft showing hyalinization and calcification. (d) Schematic representation of the extra-anatomical graft explaining the mechanism of occlusion. Proximal anastomosis dehiscence leading to the formation of a pseudoaneurysm filled with thrombotic content causing increased pressure in the surrounding tubular capsule of the graft (black arrow) and dystrophic calcification.