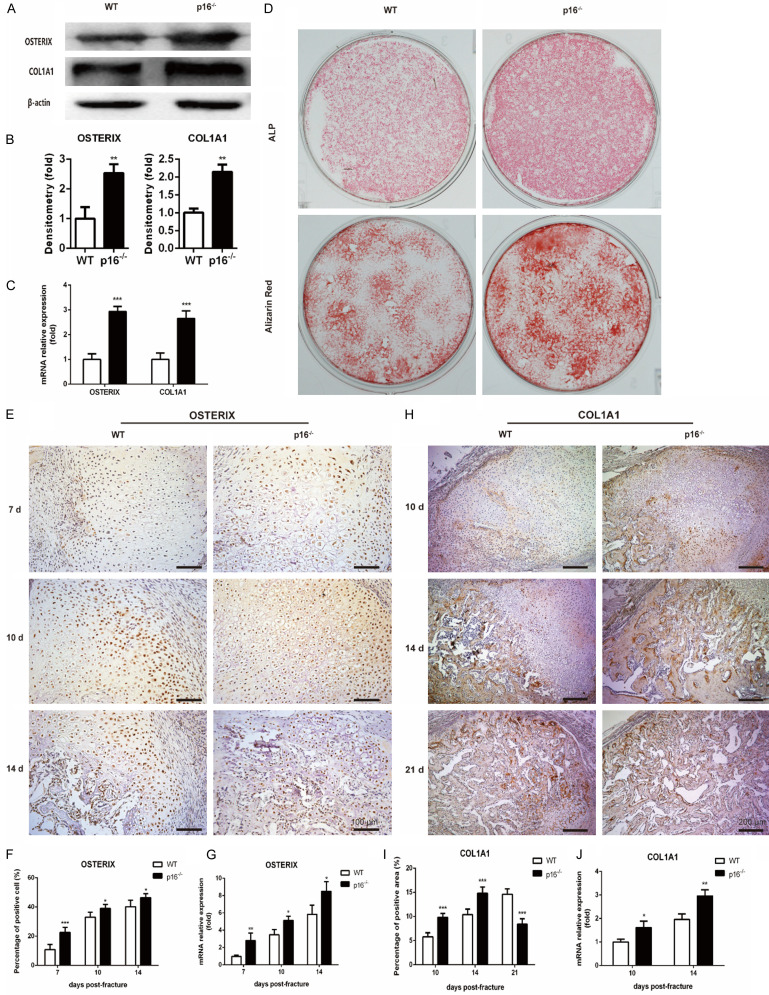
Figure 6.
Deletion of p16 facilitated osteoblastogenesis. (A) Western blot analysis was performed to determine the protein expression levels of osteoblastic differentiation markers, including OSTERIX and COL1A1 in induced BM-MSCs. β-actin was used as loading control. (B) The quantified protein levels of OSTERIX and COL1A1 in induced BM-MSCs were evaluated by densitometric analysis. (C) The mRNA levels of OSTERIX and COL1A1 in induced BM-MSCs were measured by qRT-PCR, calculated as ratio relative to GAPDH mRNA and expressed relative to WT. (D) ALP staining and alizarin red staining images of induced BM-MSCs. Representative immunohistochemical micrographs of (E) OSTERIX in callus on postoperative days 7, 10 and 14, and (H) COL1A1 in callus on postoperative days 10, 14 and 21. The percentages of (F) OSTERIX-positive cells in callus on postoperative days 7, 10, and 14, and (I) COL1A1-positive areas in callus on postoperative days 10, 14, and 21. The mRNA levels of (G) OSTERIX in callus on postoperative days 7, 10, and 14, and (J) COL1A1 in callus on postoperative days 10 and 14 were measured by qRT-PCR, calculated as ratio relative to GAPDH mRNA and expressed relative to WT. n=4, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, compared with WT mice.