Figure 10. The R267H variant of Tmem2 exhibits hypomorphic activity in the context of AVC differentiation.
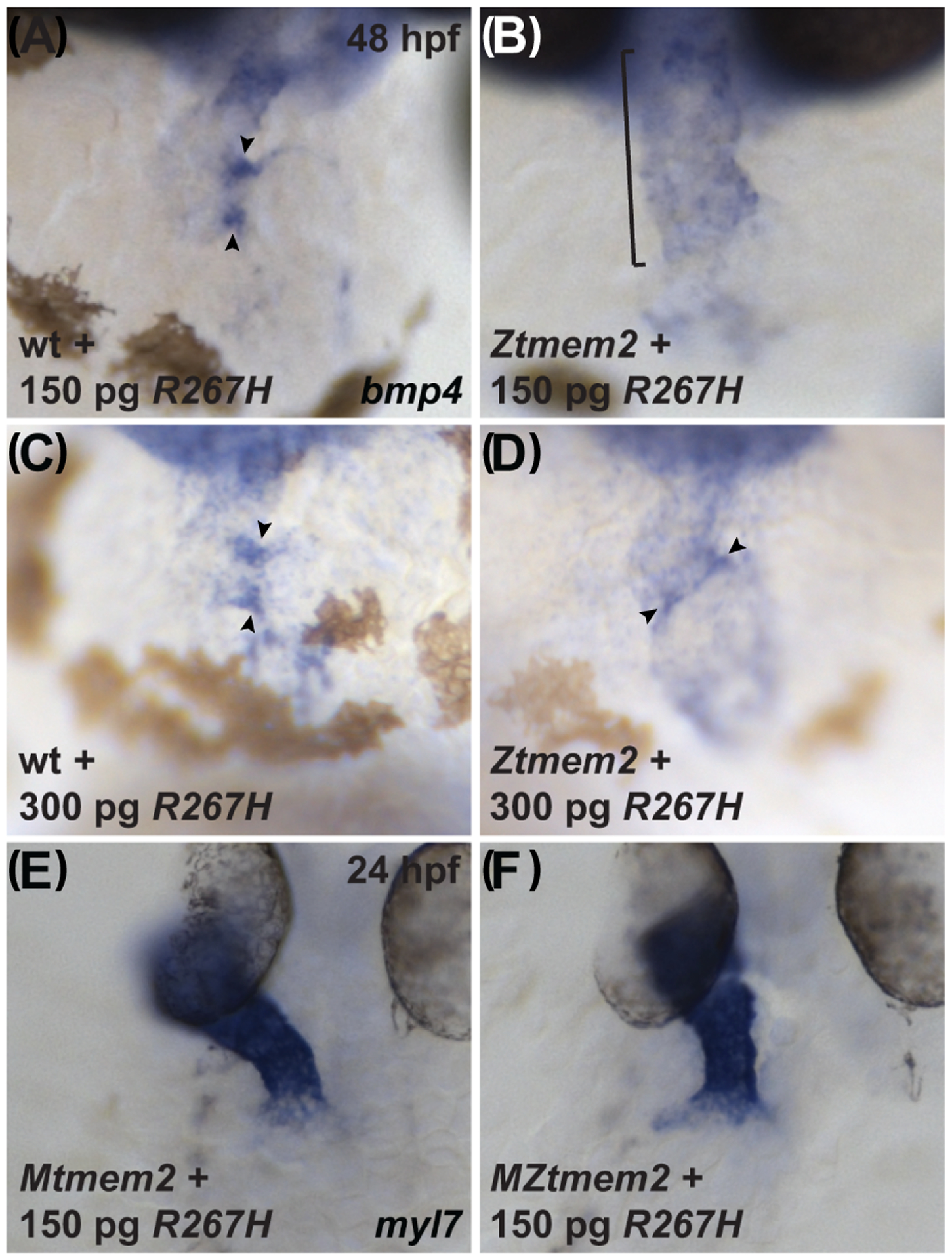
Expression of bmp4 in wt (A,C) and Ztmem2 mutant (B,D) embryos at 48 hpf, as in Fig. 2, and expression of myl7 in Mtmem2 (E) and MZtmem2 (F) mutant embryos at 24 hpf, as in Fig. 4. Injection of 150 pg of R267H mRNA does not significantly alter the bmp4 expression pattern in Ztmem2 mutant embryos (B, bracket; Table 1), whereas doubling the dosage of R267H mRNA to 300 pg can rescue the bmp4 expression pattern in a majority of Ztmem2 mutants (D, arrowheads; Table 5). Injection of either dose of R267H mRNA does not affect the bmp4 expression pattern in wt siblings (A, C, arrowheads; Tables 1 and 3). In contrast to its limited activity in the context of AVC differentiation, injection of 150 pg of R267H mRNA efficiently rescues the cardiac fusion defects in MZtmem2 mutants (F; Table 2). Expression of R267H does not alter cardiac fusion in Mtmem2 siblings (E; Table 2).
