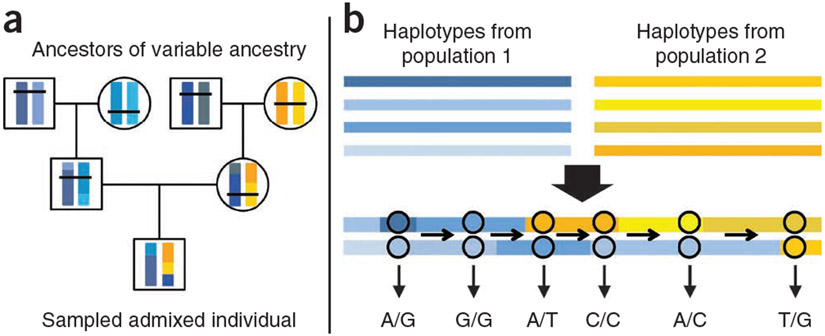
Figure 1.
Sketch of the haplotype-copying Hidden Markov model used to detect ancestry switch points. (a) Yellow and blue represent the chromosomal segments of different ancestry and the shades of each color represent different haplotypes from each ancestry. Recombination creates a mosaic of haplotypes regardless of origin but recombination events between haplotypes of different ancestries leave signatures that can be detected in descendant, admixed individuals. (b) The genotypes observed for such an individual form observed states of a Hidden Markov model in which underlying states are based on which haplotypes from a reference population each allele of the genotype is copied.