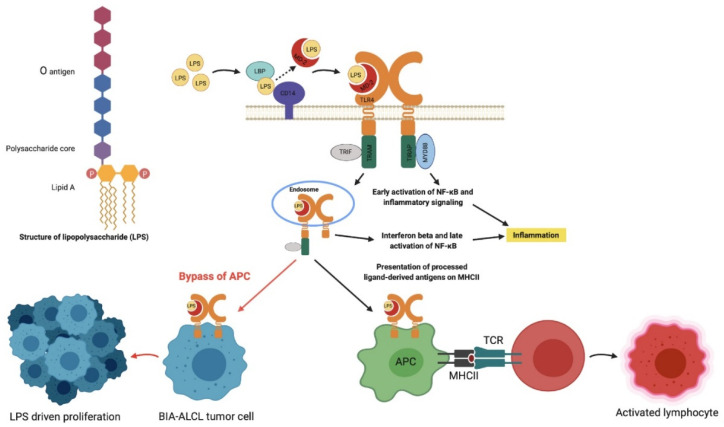
Figure 7.
Proposed mechanism of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) activation in BIA-ALCL via TLR4 pathway. LPS activation of BIA-ALCL cells occurs through an alternative TLR4 pathway rather than T-cell receptor activation whereby the cells no longer require antigen presentation and processing by an APC. This complex is then able to directly activate T-cells, producing a downregulation of the immune response as a means to increase bacterial survival. LBP: LPS binding protein; MD2: myeloid differentiating protein 2; CD14: cluster of differentiation 14; TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4; TRIF: TIR domain-containing adaptor inducing interferon beta; TRAM: TRIF-related adaptor molecule; TIRAP: Toll-interleukin 1 receptor domain-containing adaptor protein; MyD88: myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; MHCII: major histocompatibility complex 2; APC: antigen presentation cell; TCR: T-cell receptor. Figure created with BioRender.com, accessed on 26 November 2020.