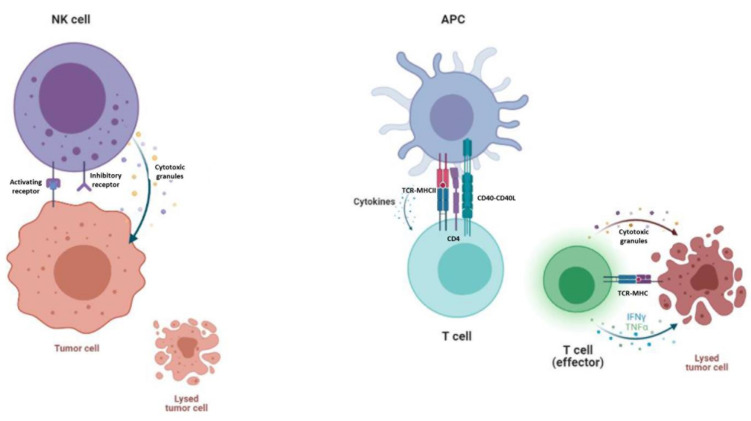
Figure 2.
Mechanism of action of NK cells and T cells. On the left, NK cells are killing a tumor cell, as inhibitory receptors do not encounter self-recognition in other cells. NK cells secrete granulocytes such as perforin and granzyme in order to kill the tumor cell. On the right, a T cell is being primed for activation by APC and cytokine stimulation. An effector T cell kills the tumor cell by secreting granulocytes and other cytokines into the tumor microenvironment.