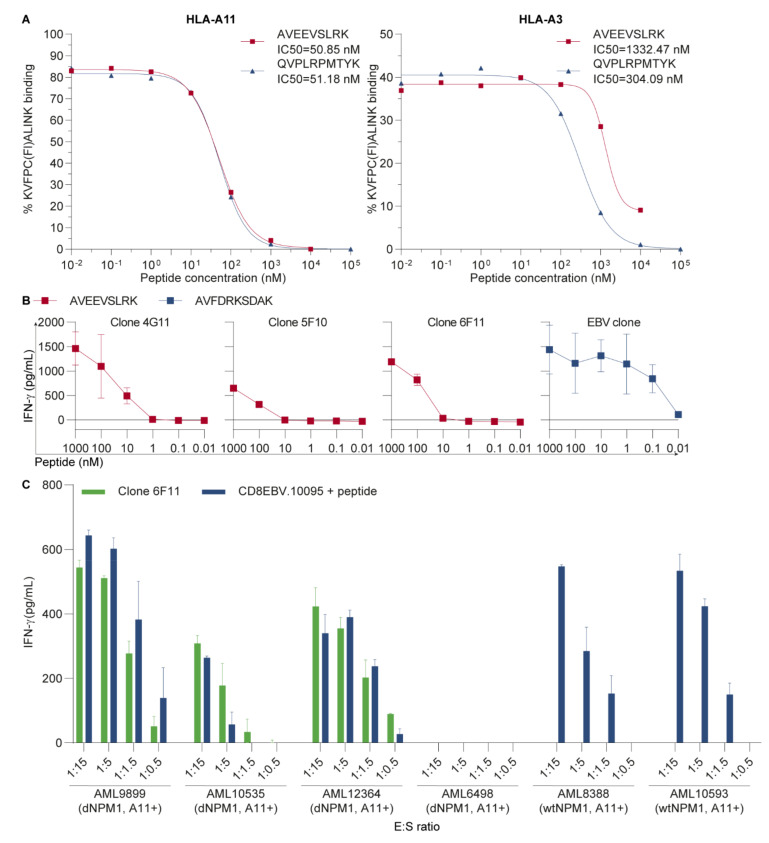
Figure 1.
Clone 6F11 specifically recognizes dNPM1-derived AVEEVSLRK in HLA-A11. (A) Affinity of AVEEVSLRK for HLA-A*11:01 (HLA-A11) (left panel) and -A*03:01 (-A3) (right panel) was measured by a competition-based peptide-HLA class I binding assay in which fluorescein-labeled KVFPC(Fl)ALINK and soluble HLA-A11 or -A3 were added to 10-fold dilutions of AVEEVSLRK (red line and squares) or QVPLRPMTYK (blue line and triangles), which is an human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) positive control peptide that binds to HLA-A11 as well as HLA-A3. After overnight incubation, fluorescence was measured by HPLC with a fluorescence detector and % binding of KVFPC(Fl)ALINK was calculated. High-affinity binding was observed for AVEEVSLRK in HLA-A11 with an IC50 of 51 nM, which is similar to the IC50 of 51 nM for the positive control. Binding of AVEEVSLRK to HLA-A3 was lower, with an IC50 of 1332 nM as compared with the positive control with an IC50 of 304 nM; (B) Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from HLA-A11+ healthy individuals were stained with peptide-HLA tetramers (pHLA-tetramers) consisting of AVEEVSLRK in HLA-A11, and tetramer+ CD8 T-cells were single-cell sorted by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). Expanded T-cell clones were incubated overnight with HLA-A11-transduced T2 cells pulsed with titrated concentrations of AVEEVSLRK (red lines and squares) at an effector:stimulator (E:S) ratio of 1:7.5. IFN-γ secretion was measured by ELISA. Clones 4G11, 5F10 and 6F11 produced IFN-γ after coculture and required higher peptide concentrations than the control T-cell clone recognizing the Epstein–Barr virus (EBV)-derived peptide AVFDRKSDAK in HLA-A11 (blue line and squares). Symbols represent mean ± SD of duplicate wells; (C) T-cell clone 6F11 was tested for recognition of 6 HLA-A11+ primary acute myeloid leukemias (AMLs) at different E:S ratios. After overnight incubation, IFN-γ production was measured by ELISA. Clone 6F11 (green bars) reacted against three of four AMLs with mutated nucleophosmin 1 (dNPM1), while dNPM1 AML6498 and two AMLs with wild type NPM1 (wtNPM1) were not recognized. CD8 T-cells from donor 10095 transduced with an EBV-specific T-cell receptor (TCR) for AVFDRKSDAK in HLA-A11 (blue bars), which were included as positive control, also failed to recognize AML6498 after loading with 500 nM EBV peptide, whereas clear reactivity was observed against the other five peptide-loaded AMLs. Bars represent mean + SD of duplicate wells.