Figure 1.
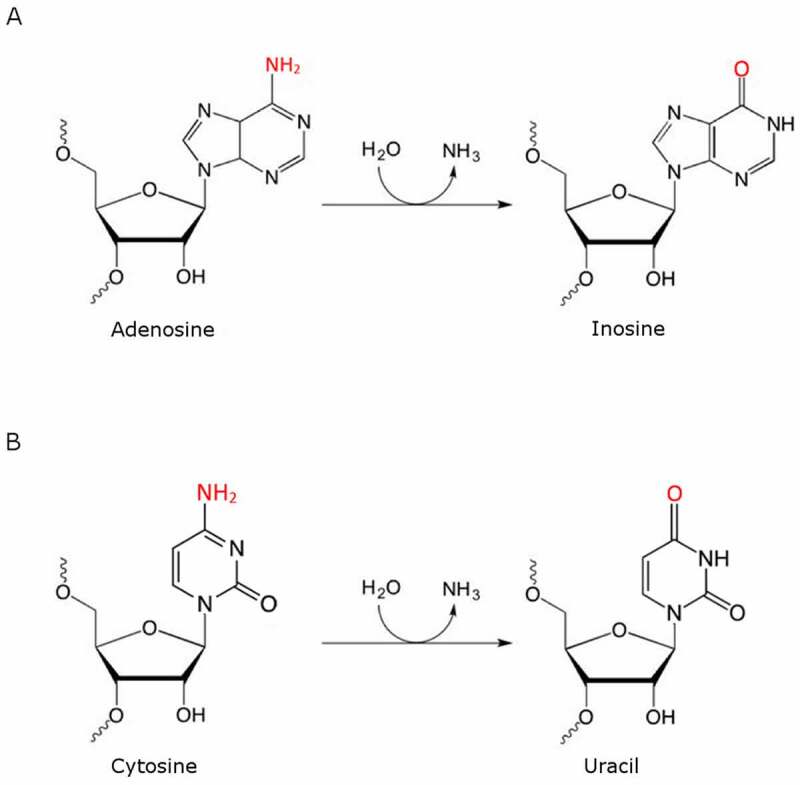
The scheme of A-to-I (A) and C-to-U (B) deamination. Deamination, catalysed by enzymes called deaminases, is the process of removing an amino group from a molecule, usually with the amino group being released as ammonia. (A) ADARs mediate the adenosine deamination process on C6 (amino group at C6 position is marked in red) which results in inosine formation. During translation inosine is recognized as guanosine and thus a different amino acid can be incorporated into the protein during its synthesis. (B) C-to-U deamination mediated by APOBECs is a very similar hydrolytic deamination reaction where cytosine is converted to uracil; this change can also recode protein open reading frames. The A-to-I and C-to-U deaminases are distantly evolutionarily related to each other and share similar zinc-containing active sites
