Table 1.
Schematic representation of the six distinct studies on developing splice-modulating AOs targeting cancers. Among these AOs, (1) SSO111, (2) Acr-PNA 2794, (3) SSOe26, and (6) morpholino MDM4 inhibited overexpression of oncogenes by inducing exon skipping, thus producing non-functional variants or leading to nonsense-mediated decay (NMD) of mRNA, while (5) PNA 4577, 4578, 4580 and 4581 predominantly induced intron retention, resulting in the production of non-functional variants. Besides, (4) ASWT1exon5 induced RNase H-mediated degradation of longer transcripts, thus increasing the proportion of naturally occurring, shorter transcripts which exclude an important exon. 2′-MOE, 2′-O-methoxyethyl; 2′-OMe, 2′-O-methyl; PNA, peptide nucleic acid; LNA, locked nucleic acid; PS, phosphorothioate; PMO, phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer.
| No. | Research | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|
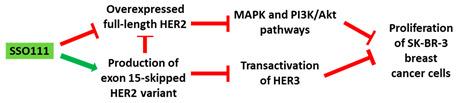
| 1 | AO | SSO111 is a 20mer fully modified 2′-MOE-PS AO-targeting oncogene HER2. SSO111 induced exon 15 skipping during splicing, leading to the generation of a novel mRNA transcript that excludes exon 15.
|
[81] |
| Mechanism |
|
||
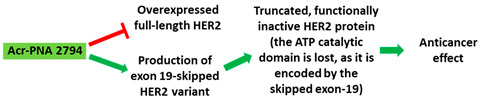
| 2 | AO | Acr-PNA 2794 is a 15mer fully modified PNA AO conjugated with Acr targeting HER2. Acr-PNA 2794 induced exon-19 skipping, leading to the generation of a novel mRNA transcript that excludes exon-19.
|
[82] |
| Mechanism |
|
||
| 3 | AO | SSOe26 is a 15mer LNA-modified mixmer AO targeting HER4. SSOe26 induced exon 26 skipping, leading to the generation of a novel mRNA transcript that excludes exon 26 (CYT2 isoform).
|
[85] |
| Mechanism |
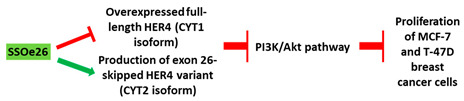
|
||
| 4 | AO | ASWT1exon5 is a 20mer 2′-MOE-PS gapmer AO targeting oncogene WT1. It induces RNase H-mediated degradation of exon 5-containing transcripts, thus increasing the proportion of transcripts that exclude exon 5.
|
[91] |
| Mechanism |
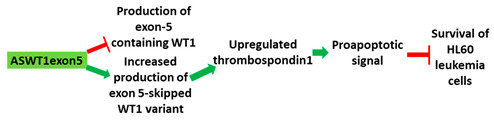
|
||
| 5 | AO | PNA 4577, 4578, 4580, and 4581 are 16mer fully modified PNA AOs conjugated with octaarginine or cholic acid-targeting oncogene TdT. These four PNAs all induced intron 7 retention, leading to the generation of a novel mRNA transcript that included intron-7.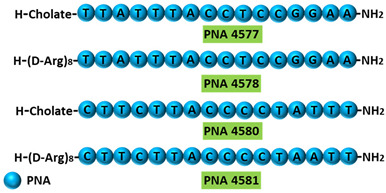
|
[95] |
| Mechanism |
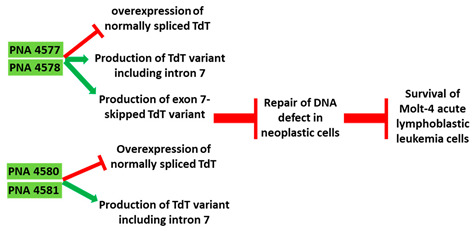
|
||
| 6 | AO | Morpholino MDM4 is a 25mer fully modified PMO AO targeting MDM4. Morpholino MDM4 induced exon 6 skipping, leading to nonsense-mediated decay of the mRNA transcript that excludes exon-6.
|
[98] |
| Mechanism |

|
||
