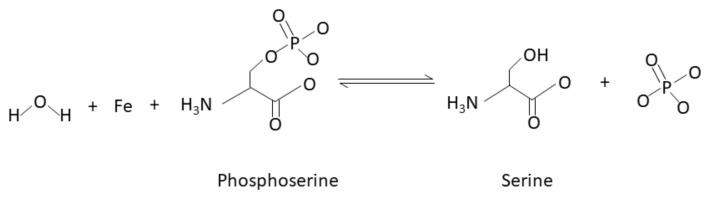
Figure 3.
Chemical equation of dephosphorylation of a serine residue by an iron atom located in the CaN-active site adapted from Kissinger et al. (1995). A water molecule is deprotonated by the iron atom, followed by a hydrolysis reaction between the deprotonated (activated) water molecule and phosphorylated serine residue (phosphoserine). This reaction yields serine and phosphate. Threonine substrates follow a similar mechanism of water activation and dephosphorylation [16].