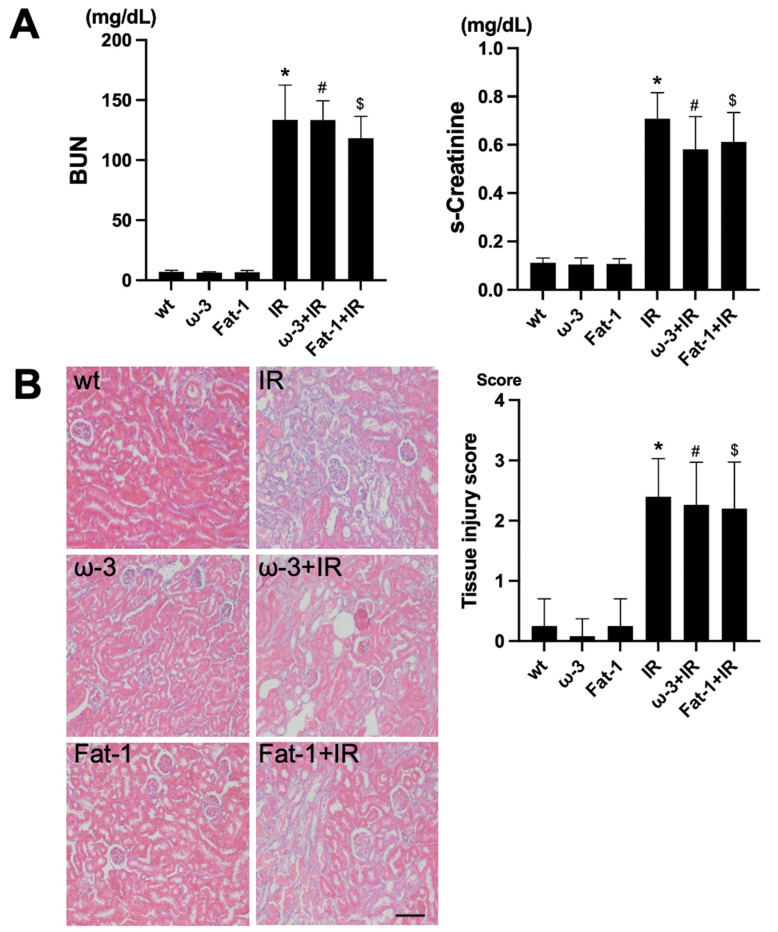
Figure 1.
Renal function and histology in ischemia-reperfusion (IR) kidney. (A) The levels of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and serum creatinine (s-Cr) were significantly increased in IR mice compared to wt mice. ω-3+IR mice also had higher BUN and s-Cr levels as compared to ω-3 mice, and Fat-1+IR mice also had higher BUN and s-Cr levels as compared to Fat-1 mice. (B) Representative kidney section with H&E stain; renal injury tissue represents cell debris, tubular necrosis, and inflammatory cells. Original magnification, 200×. Scale bar = 50 μm. * p < 0.001 vs. wt, # p < 0.001 vs. ω-3, $ p < 0.001 vs. Fat-1. The bar represents mean ± S.D. (wt, wild-type sham; ω-3, ω-3 PUFA oral administration sham; Fat-1, Fat-1 induction sham; IR, IR renal injury in wild-type mice; ω-3+IR, IR renal injury in ω-3 PUFA oral administration mice; Fat-1+IR, IR renal injury in Fat-1 induction mice).