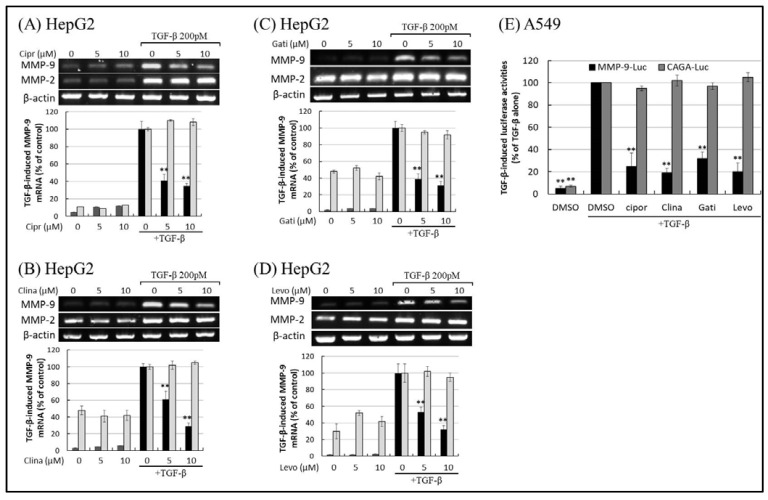
Figure 4.
Fluoroquinolones (FQs) inhibit transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β)-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) transcriptional activity and gene expression. MMP-9 and MMP-2 gene expression in cells exposed to FQs and TGF-β was detected by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). HepG2 cells were pre-incubated with different concentrations of ciprofloxacin (A), clinafloxacin (B), gatifloxacin (C), and levofloxacin (D) for 30 min before stimulation with 200 pM TGF-β. The images shown are representative of three independent experiments with similar results. (E) Promoter assays in cells exposed to FQs and TGF-β, similar to RT-PCR. Firefly and renilla luciferase activity were measured in cells co-transfected with MMP-9-Luc, CAGA-Luc, and pRL-CMV and incubated in the presence or absence of FQs and TGF-β. MMP-9 and CAGA firefly luciferase activity was normalized to renilla luciferase activity, and the intensity of the luciferase signal in the treatment groups was expressed as a percentage of that measured in the TGF-β-stimulated experiments. Results are presented as means ± standard deviation (error bars) of three independent experiments. Statistically significant differences (** p ≤ 0.001) were observed between cells treated with TGF-β-stimulated controls and those treated with TGF-β and FQs.