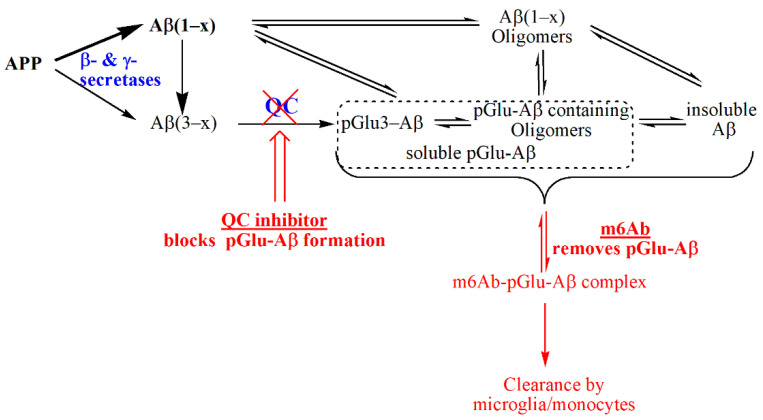
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of the molecular pathways for reduction of pGlu3-Aβ by QC inhibition and anti-pGlu3-immunotherapy (m6Ab). The current study supports the concept that both strategies act independently and are additive. The formation of pGlu-Aβ occurs after APP cleavage by sheddases such as BACE1 or meprin β, which may lead directly to N-truncated Aβ forms and the pGlu3-Aβ precursor, Aβ(3–x). While QC inhibition prevents de novo-synthesis of pGlu3-Aβ, which reduces formation of toxic oligomers and coaggregation with other Aβ forms, the pGlu3-Aβ specific antibody prevents aggregation and elicits clearance of extracellular, soluble pGlu3-Aβ containing aggregates by opsonization and phagocytosis by microglia and/or monocytes.