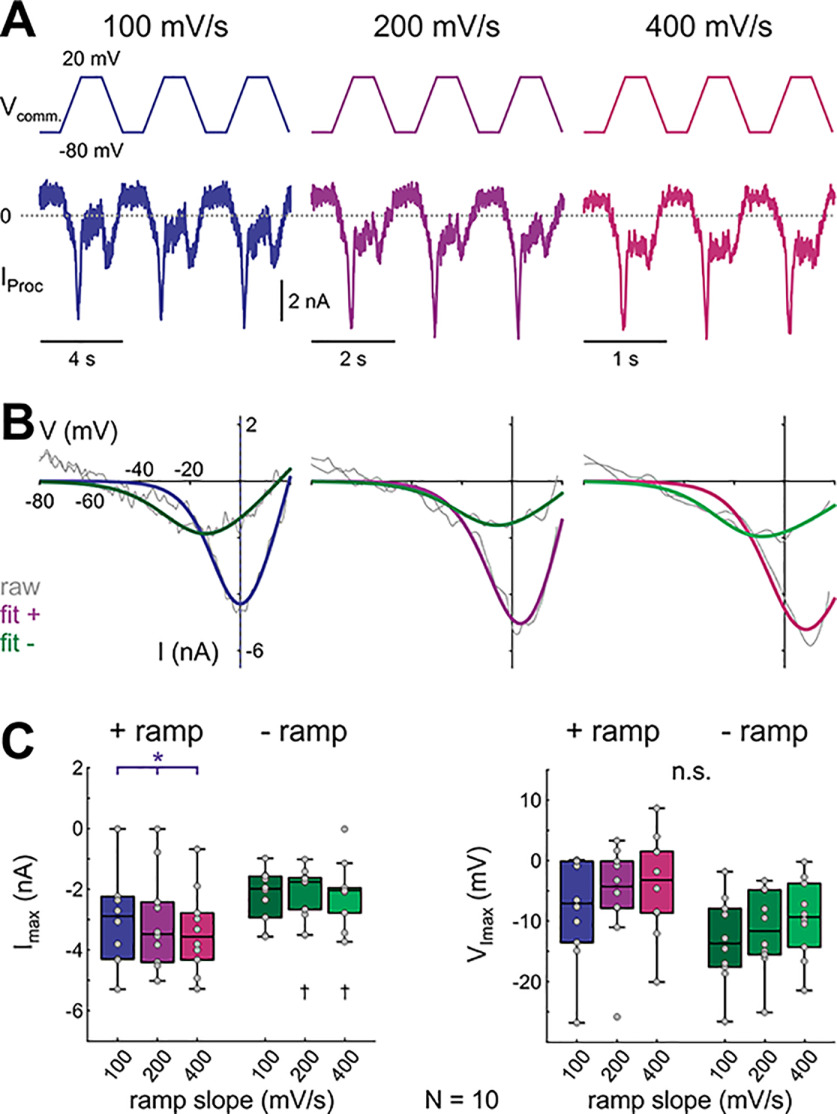
Figure 4.
Steady-state levels of the proctolin-activated currents elicited by a periodic ramp-and-hold stimulus depend on ramp slope and direction. A, Proctolin-activated currents (IProc) in response to the last three of 30 sweeps of ramp-and-hold stimuli with different slopes (color-coded). Data are from the same experiments as Figure 3A. B, Steady-state I-V curves for different ramp slopes (color-coded) from one experiment (same experiment as in A). Gray lines show raw current recordings, colored lines show logistic fits that were used to smoothe the raw data. C, Quantitative analysis of Imax (left) and VImax (right) for different ramp slopes and ramp directions (N = 10). Dots represent data from individual experiments. Imax is sensitive to ramp slope on the + ramp but not to the – ramp (two-way RM ANOVA; Table 1; results in Extended Data Fig. 4-1). Asterisks indicate significant differences between slopes within the same direction, daggers indicate significant differences between directions within the same slope at α = 0.05. n.s. indicates no significant changes.