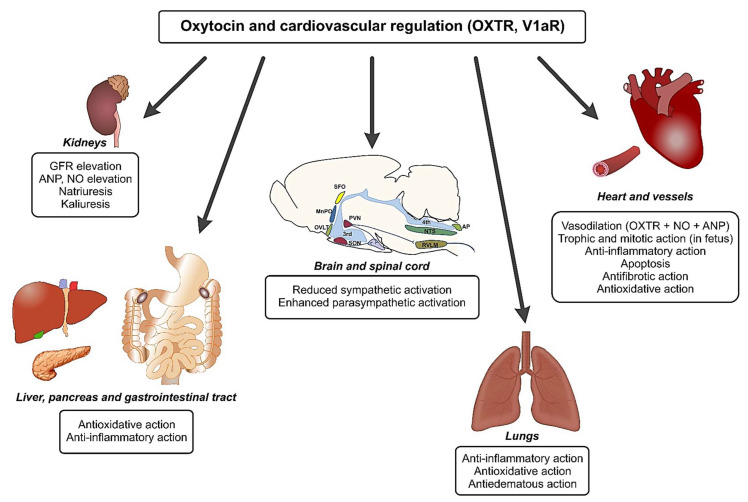
Figure 2.
The role of oxytocin in cardiovascular regulation. Oxytocin stimulates specific receptors (OXTR) and vasopressin receptors (V1aR) in different organs. In the central nervous system, it regulates the activity of several groups of neurons and may exert either stimulatory or inhibitory effects, depending on the site of action. The predominant effects of the action of oxytocin in the central nervous system involve reduced activation of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system and enhanced activation of the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. Abbreviations: AP—area postrema; MnPO—median preoptic nucleus; NTS—nucleus tractus solitarii; OVLT—organum vasculosum of the lamina terminalis; PVN—paraventricular nucleus; RVLM—rostral ventrolateral medulla; 3rd—third ventricle; 4th—fourth ventricle.