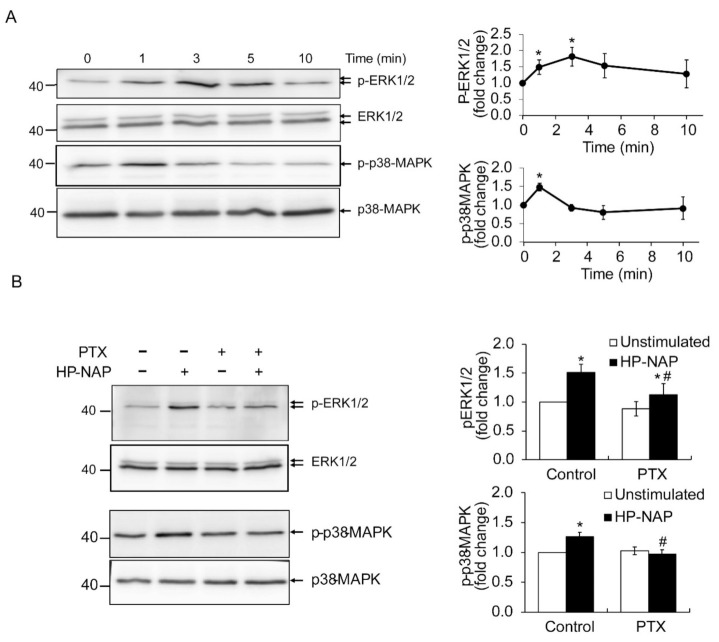
Figure 3.
Involvement of PTX-sensitive G-proteins in HP-NAP-induced activation of ERK1/2 and p38-MAPK in ATRA-induced differentiated HL-60 cells. (A) HP-NAP-induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and p38-MAPK in ATRA-induced differentiated HL-60 cells. ATRA-induced differentiated HL-60 cells at a density of 2.5 × 106 cell/mL were stimulated with 1 μM HP-NAP or D-PBS, pH 7.2, as the unstimulated control at 37 °C for the indicated time. The cells were lysed and whole cell lysates were applied to immunoblot analysis for phospho-ERK1/2, ERK1/2, phospho-p38-MAPK, and p38-MAPK. Quantitative data are expressed as the fold change by defining the amounts of the phosphorylated proteins in unstimulated control cells as 1 and as mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. (B) Effect of PTX on HP-NAP-induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and p38-MAPK in ATRA-induced differentiated HL-60 cells. ATRA-induced differentiated HL-60 cells at a density of 5 × 106 cell/mL were pretreated with 100 ng/mL PTX or the vehicle control at 37 °C for 16 h and followed by the stimulation with 1 μM HP-NAP or D-PBS, pH 7.2, as the unstimulated control at 37 °C for 3 min to examine the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 or 1 min to examine the phosphorylation of p38-MAPK. The cells were lysed and whole cell lysates were applied to immunoblot analysis as described in A. Quantitative data are expressed as the fold change described in A and as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *: p value < 0.05 as compared with unstimulated cells with in each group; #: p value < 0.05 as compared with HP-NAP-stimulated control cells.