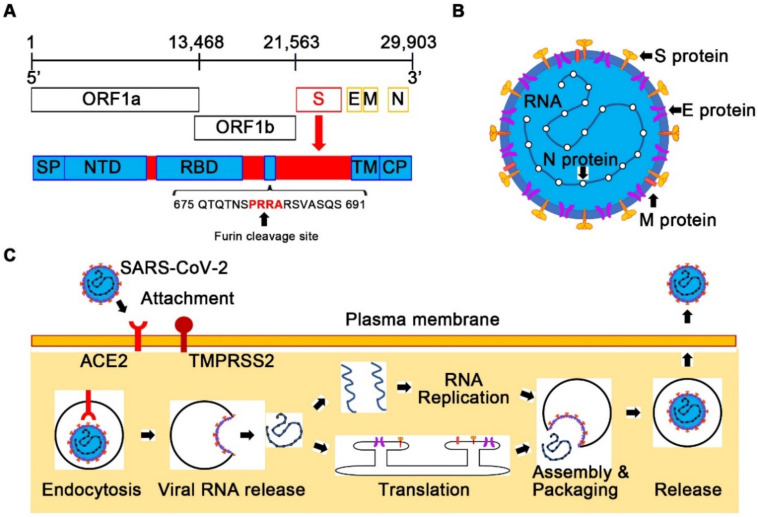
Figure 1.
Genome composition, structure, and life-cycle of SARS-CoV-2. (A) Genome composition of SARS-CoV-2. The genome of SARS-CoV-2 is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA. Nonstructural proteins involved in genome transcription and replication are encoded in the open reading frame 1a (ORF1a) and ORF1b. The four ORFs encode the main structural proteins: the spike (S), envelope (E), membrane (M), and nucleocapsid (N) proteins. The S protein has the insertion of four amino acid residues (PRRA) that generate a polybasic cleavage site (RRAR). CP, cytoplasmic domain; NTD, N-terminal domain; RBD, receptor-binding domain; SP, signal peptide; TM, transmembrane domain. (B) Structure of SARS-CoV-2. SARS-CoV-2 virion consists of the envelope with three structural proteins, such as the S, E, M proteins, and the genomic RNA with the N proteins. (C) Life-cycle of SARS-CoV-2. SARS-CoV-2 enters host cells via its host cellular receptor, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). The transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2) cleaves and primes the receptor-bound S protein of SARS-CoV-2 for membrane fusion, which results in the release of the viral RNA genome into the cytoplasm. Translated viral structural proteins and replicated genomic RNA are assembled into the newly formed viral particles. Progeny viruses are released from the host cell by exocytosis.