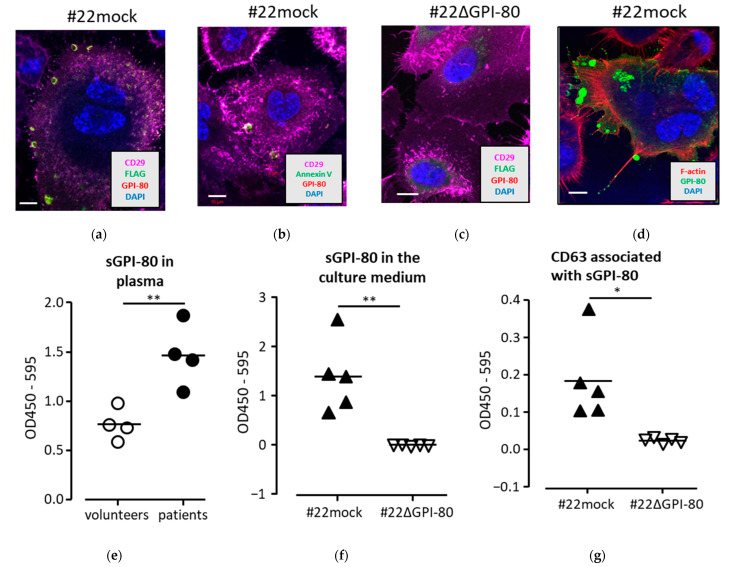
Figure 1.
Localization of GPI-80 on PC3 transformant. (a–d) GPI-80 was observed by confocal microscopy. Cells (#22mock (a) and #22ΔGPI-80 (c)) were stained with anti-CD29 mAb (pink), anti-FLAG mAb (green), anti-GPI-80 mAb (yellow), and DAPI (blue). Cells (#22mock (b)) were also stained with anti-CD29 mAb (pink), anti-GPI-80 mAb (yellow), DAPI (blue), and Annexin V (green). (d) After fixation and incubation with unlabeled anti-GPI-80 mAb (3H9) and FITC-conjugated anti-mouse antibody (green), the permeabilized #22mock cells were stained with phalloidin (red) to detect F-actin. Data are representative of results from more than three independent experiments. Scale bar, 10 μm. (e–g) Detection of soluble GPI-80 by sandwich ELISA. (e) Soluble GPI-80 level in the plasma of healthy volunteers (four volunteers; open circle) and the prostate cancer patients (four patients; closed circle) was detected by paired anti-GPI-80 mAbs, 3H9 and 4D4. (f) Soluble GPI-80 levels in the conditioned medium of #22mock (closed triangle) and #22ΔGPI-80 (open triangle) cells were also measured using paired anti-GPI-80 mAbs. (g) To detect the colocalization of GPI-80 with CD63, conditioned media from #22mock (closed triangle) and #22ΔGPI-80 (open triangle) were analyzed using anti-GPI-80 mAb (3H9) paired with anti-CD63 mAb (8A12). These culture media were independently collected from confluent cells after 4 days. Statistical significance was calculated using two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01).