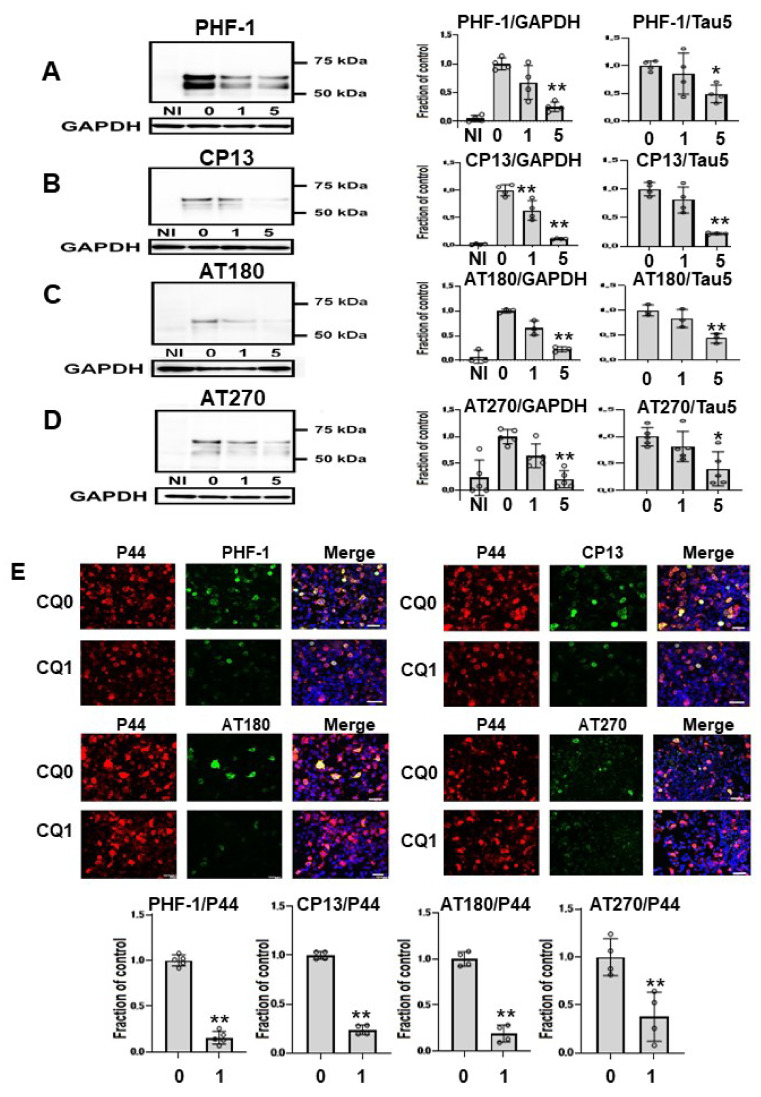
Figure 4.
Phosphorylated tau was decreased by clioquinol (CQ). Phosphorylated tau was significantly decreased by 5 μM CQ, detected by PHF-1(n = 4) (A), CP13 (n = 4) (B), AT180 (n = 3) (C), and AT270 (n = 5) (D). Phosphorylated tau detected by CP13 or AT 180 was also significantly decreased by 1 μM CQ. Bar: ± SD, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05. The ratio of phosphorylated tau to tau levels detected using non-phospho dependent Tau5 with 5 μM CQ also decreased based on antibodies against PHF-1, CP13, AT180, and AT270. Immunocytochemical study revealed that CQ (1 μM) decreased phosphorylated tau. The ratio of phosphorylated tau to tau levels detected using non-phospho dependent Tau5 with 1 μM CQ also decreased based on antibodies against PHF-1 (n = 5), CP13 (n = 4), AT180 (n = 4), and AT270 (n = 4). CQ 0: DMSO-treated cells, CQ1: 1 μM CQ-treated cells.** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05, Bar: 50 μm (E). Data from PHF-1/GAPDH, CP13/GAPDH, AT180/GAPDH, and AT270/GAPDH followed a normal distribution and were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test, and the data from PHF-1/P44, CP13/P44, AT180/P44, and AT270/P44 followed a normal distribution and were analyzed by the Student’s t-test.