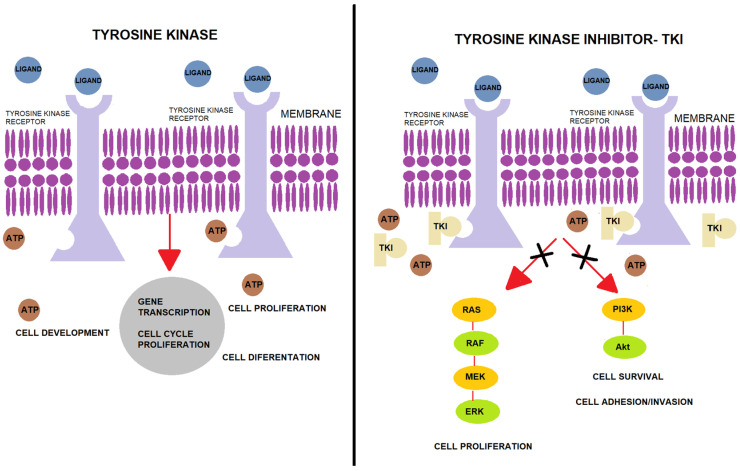
Figure 2.
Mechanism of action of tyrosine kinase and tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Normally, tyrosine kinase transfers a phosphate group from ATP to specific intracellular proteins, which is necessary for gene transcription and cell proliferation. If a TKI is attached instead of ATP, there is a disturbance in the process, which can lead to apoptosis. TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor; Akt, serine/threonine kinase 1; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinases; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; RAF, proto-oncogene; RAS, rat sarcoma virus protein family.