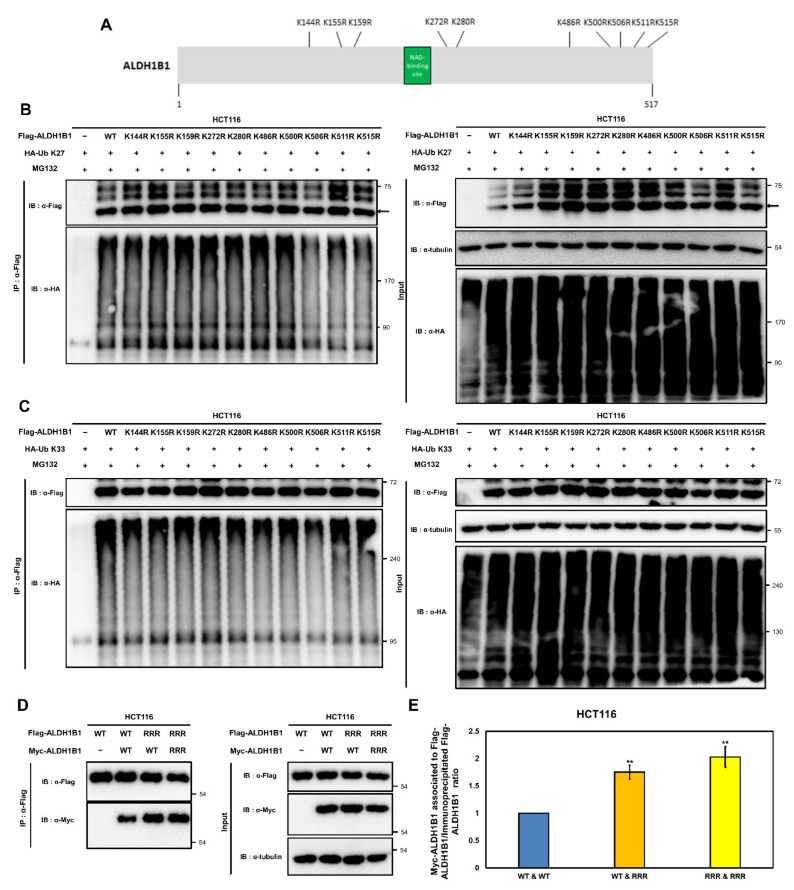
Figure 7.
Identification of K27- and K33-mediated ubiquitination acceptor sites within ALDH1B1 and its effect on the self-association of ALDH1B1. (A) Schematic diagram showing point mutations in the predicted ubiquitination sites of ALDH1B1. (B,C) K27- and K33-linked ubiquitination of ALDH1B1 WT and single lysine-mutated forms (K144R, K155R, K159R, K272R, K280R, K486R, K500R, K506R, K511R, and K515R) were investigated by immunoprecipitation. Flag-tagged WT ALDH1B1 or ALDH1B1 mutants were cotransfected with HA-tagged ubiquitin K27 or K33 into HCT116 cells. Cells were treated with 10 µM MG132 for 6 h and protein lysates were analyzed by immunoprecipitation and western blot analysis (n = 3). (D) The self-association of WT and a triple mutant construct of ALDH1B1 was analyzed by Co-IP (n = 4). (E) Quantification of the results in (D) using ImageJ. ** p < 0.01.