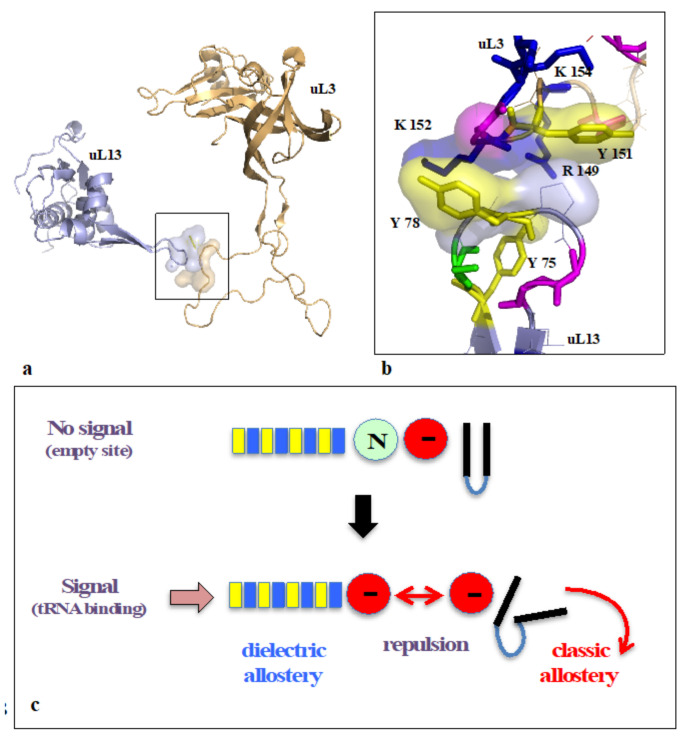
Figure 8.
Aromatic amino acids in information transfer and processing. (a,b): global and detailed view of a “molecular synapse” in bacterial large subunit r-protein network. The conserved amino acids are represented by coloured sticks. (c) Possible pathways of electrostatic signalling through an array of action-π interactions (yellow rectangles = aromatic residues and blue rectangles are basic residues). The combination of diverse allosteric modules can integrate multiple stimuli. The transient change of charge of an amino acid such as a histidine induced by its electrostatic context may induce large conformational changes (“N” = neutral and “−” = negative charge).