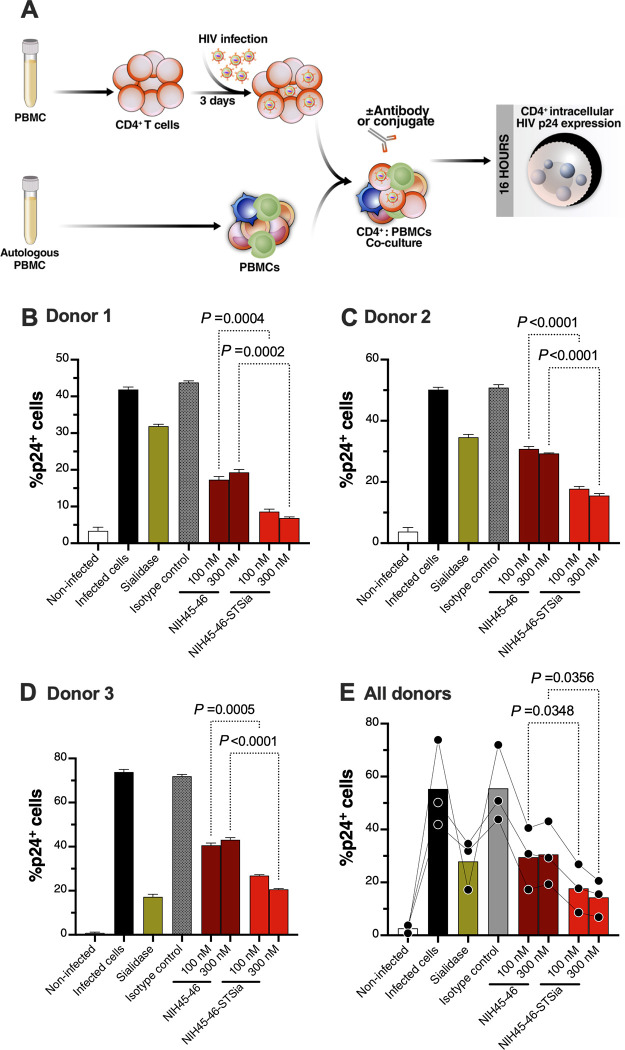
Fig 9. NIH45-46-STSia induces PBMC cytotoxicity towards autologous primary HIV-infected CD4+ T cells.
(A) A schematic representation of the workflow to evaluate the cytotoxicity of PBMC against autologous HIV-infected CD4+ T cells in the presence of bNAb or bNAb-STSia conjugate. CD4+ T cells were isolated from fresh PBMC and exposed to HIV-1 IIIB for 72 h. On the third day, virus-infected CD4+ T cells were treated or not with Sialidase, NIH45-46, NIH45-46-STSia, or isotype-matched control antibody. PBMC from the same donor were co-cultured with autologous HIV-infected CD4+ T cells for 16 h. Following overnight incubation, the mixtures were stained for live/dead viability, CD3, CD8, and intracellular p24. Percent p24+ was derived after gating on CD3+, CD8- and live cells. (B) Data from donor 1. (C) Data from donor 2. (D) Data from donor 3. (E) Average data from all donors. Assay from each donor was performed in 4 replicate wells (E:T 100:1; n = 3 donors). Statistical analyses for panels B-D were performed using unpaired ANOVA with post-hoc Dunnett T3 method (to correct for multiple comparisons) comparing the indicated groups. Statistical analysis for panel E was performed using paired ANOVA with post-hoc Holm-Sidak method (comparing the indicated conditions).