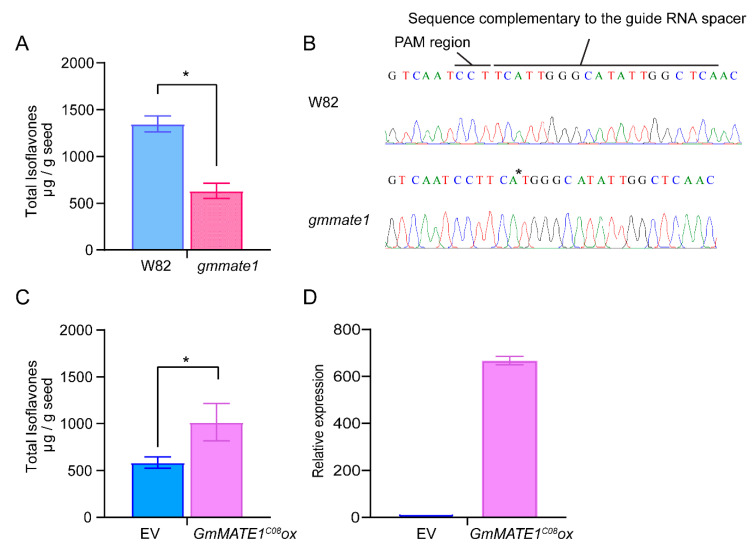
Figure 5.
GmMATE1 is responsible for determining seed isoflavone contents. (A) The total isoflavone contents in the CRISPR/Cas9-edited GmMATE1 mutant was significantly lower than those in its wild-type, W82. Values shown were the means of at least three independently collected batches of seeds ± SEM. Significant differences were determined by Mann-Whitney test. *, p < 0.05. (B) The mutation site in the GmMATE1C08 gene, with the single-nucleotide deletion marked with an asterisk. (C) The levels of isoflavones in the transgenic soybean overexpressing GmMATE1C08 were significantly higher than those in the empty vector control, both in the W82 background. Values shown were the means of four independently collected batches of seeds ± SEM. Significant differences were determined by Mann-Whitney test. *, p < 0.05. (D) Relative expression levels of GmMATE1 in the GmMATE1C08-overexpressor and the empty vector control in the W82 background. The expression levels were normalized to the reference gene, VPS, using the 2−ΔΔCt method.