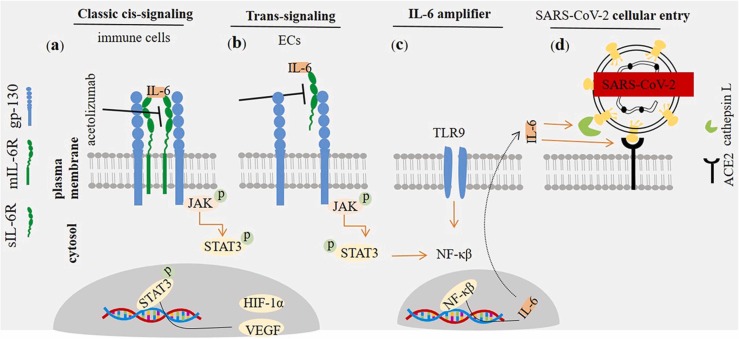
Fig. 1.
Interleukin (IL)−6 receptor/ligand interactions. IL-6 interacts with two types of IL receptors (IL-6Rs): (a) Interaction with membranous form directs classic cis-signaling pathway, whereas interaction with the soluble form (i.e. sIL-6R) promotes trans-signaling pathway (b). The trans-membrane protein gp-130 acts as a subunit for IL-6R, transducing signals toward cytosol. IL-6/IL-6R/gp-130 interactions transduce signals via janus kinas (JAK) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3). STAT3 is further transferred toward the nucleus in order to promote activation of target gens, such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)−1α. Inhibition of membrane-bound and soluble IL-6Rs by agents like acetolizumab is of therapeutic importance in cancer patients and cases with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) induced disease. (c) Interleukin (IL)−6 amplifier in patients with SARS-CoV-2 induced disease. The activity of NF-κβ is induced by IL-6/STAT-3. NF-κβ, in turn, promotes IL-6 transcription and its release toward the extracellular milieu. This mechanism of implication will intensify the severity of condition in patients with high activity of IL-6, such what seen in SARS-CoV-2 induced disease. (d) IL-6 inducible effect on SARS-CoV-2 cellular entry. SARS-CoV-2 interacts with angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor in order to enter the cellular cytosol. Recognition of the ACE2 by the virus and its membrane infusion is mediated by cathepsin L. IL-6 induces the activity of ACE2 and cathepsin L, thus facilitating cellular entry of the virus.