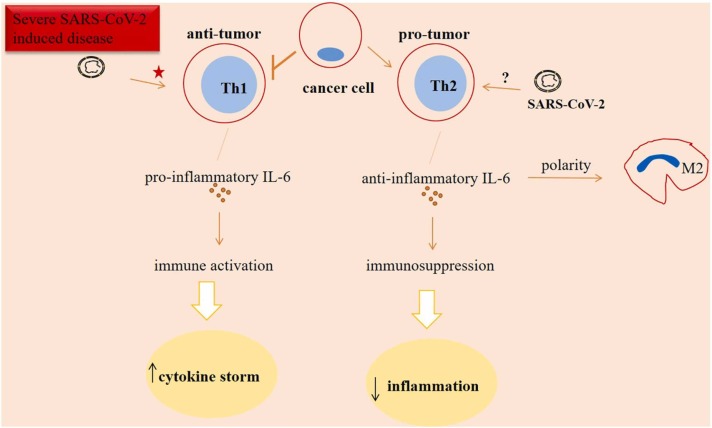
Fig. 5.
Interleukin (IL)−6 in cancer patients who also have SARS-CoV-2 induced disease. The activity of anti-tumor T helper 1 (Th1) cells is reduced in tumors. By contrast, pro-tumor Th2 cells are active and promote anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive signals. The resultant immunosuppression is indicative of lower extent of cytokine storm, and presumably lower extent of SARS-CoV-2 related damages in cancer patients. Th1 cells represent a hyperactive state in response to the factors like IL-6 released as a response to the severe SARS-CoV-2 induced disease, rendering systemic antiviral responses. However, a hyperactive cell type generally shows an exhausted state, which means the final decapitation for T cell-based immunity. Signals from T cells seen in patients with SARS-CoV-2 induced disease may be an explanation for further immunosuppression. Taken together, it seems that cancer patients are at the higher risk of experiencing damages due to SARS-CoV-2 compared with non-tumor patients who have active SARS-CoV-2 induced disease. Another interpretation is that SARS-CoV-2 may change tumor ecosystem into a more aggressive phenotype. Star indicates a hyperactive state, and the question mark represents uncertainty of the SARS-CoV-2 action on Th2 cell activity.