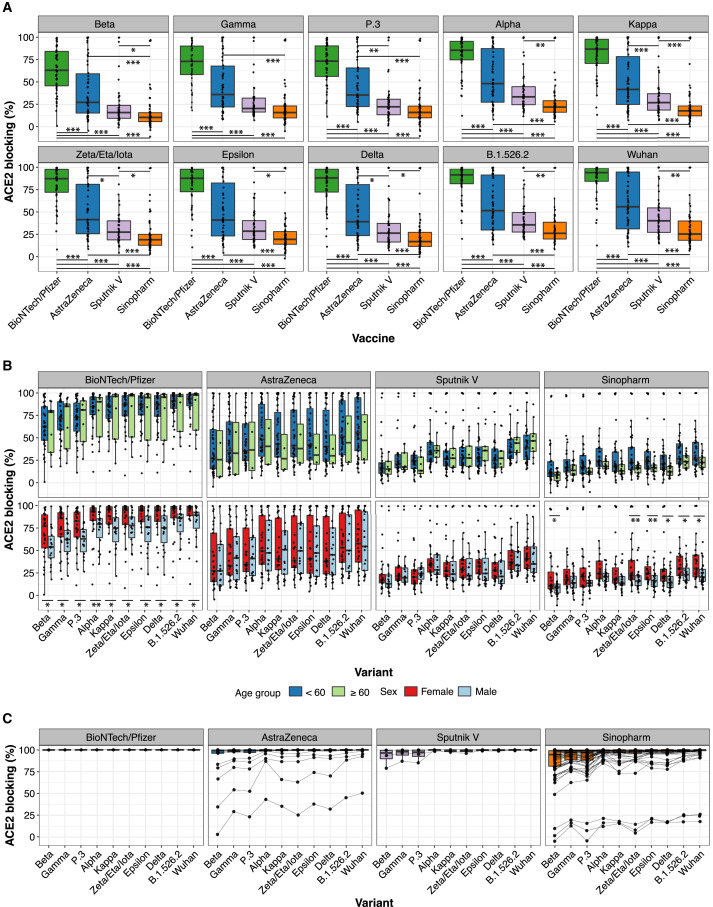
Figure 1.
Vaccine-induced antibody blocking of RBD-ACE2 binding for different viral variants
(A) Percentage blocking of ACE2 binding to RBD of specified viral variants by plasma antibodies of recipients of Pfizer/BioNTech, AstraZeneca, Sputnik V, and Sinopharm vaccines is shown. Significance of differences between pairwise combination of vaccine groups was calculated by Wilcoxon test with Bonferroni correction to adjust for multiple hypothesis correction (∗, ∗∗, and ∗∗∗ indicate p < 0.05, p < 0.01, and p < 0.001 respectively).
(B) Blocking antibody responses stratified by participant age (< 60 years, or ≥ 60 years) and sex. Significance between two groups (age groups and male versus female) was calculated by Wilcoxon test (∗ and ∗∗ indicate p < 0.05 and p < 0.01 respectively).
(C) RBD-ACE2 blocking antibody responses for 99 participants with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection post-vaccination with the indicated vaccines. Data points for samples from the same individual are connected with a line.