Figure 1. Posttranslational modifications examined using peptide and/or protein synthesis.
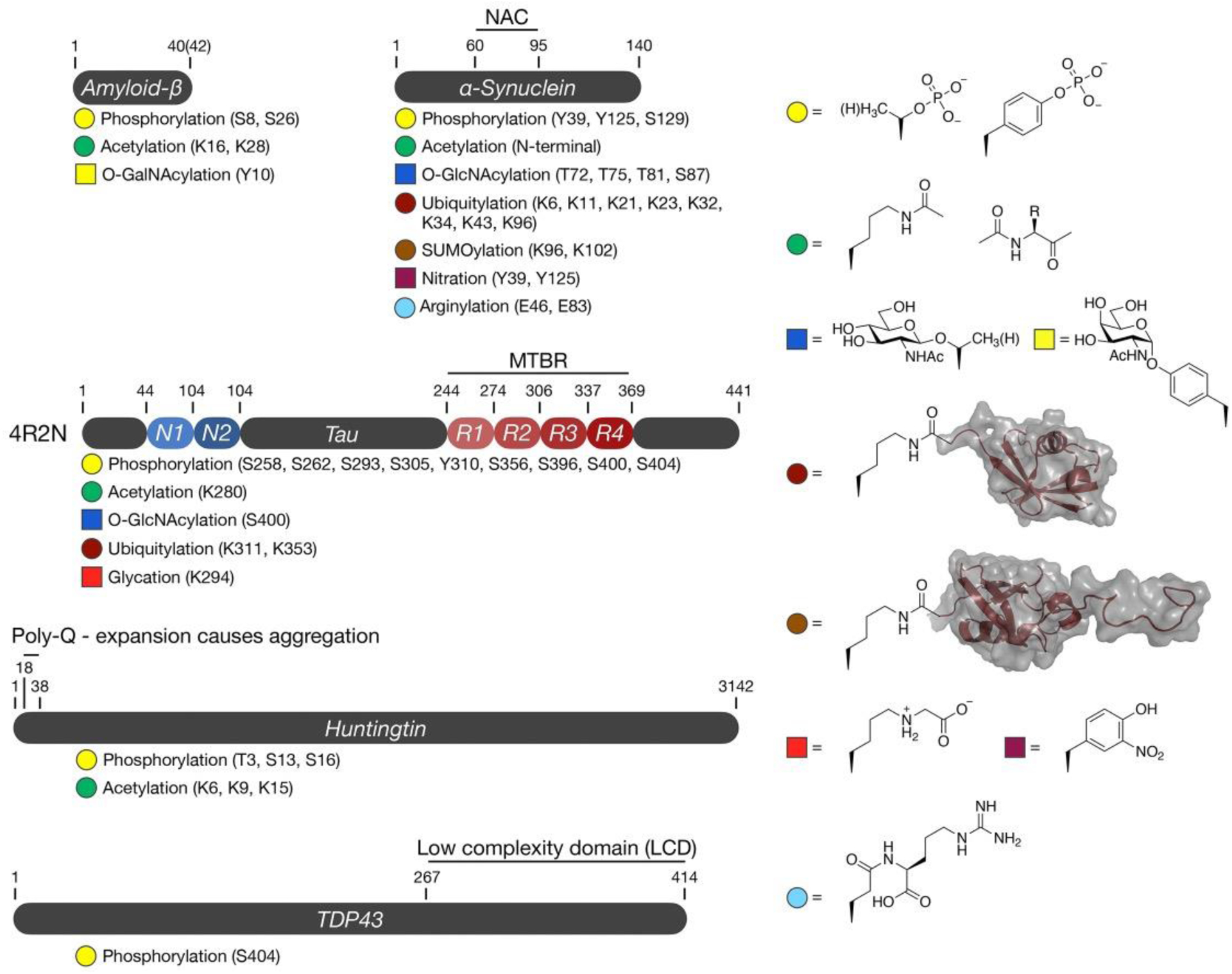
Aβ is a short peptide prone to amyloid aggregation in Alzheimer’s disease. αSyn is a short protein with a central, hydrophobic NAC (non-amyloid component) required for amyloid formation in Parkinson’s disease. Tau is expressed as a mixture of isoforms containing different numbers of N-terminal (N) and microtubule binding repeats (R). The MTBR (also called the MTBD) is responsible for driving Tau aggregation in Alzheimer’s disease. Hutingtin is a very large scaffolding protein that forms amyloids in Huntington’s disease upon expansion of a polyglutamine (poly-Q) track in its N-terminus. TDP43 forms aggregates in ALS due to its low complexity domain (LCD)
