Figure 2. Dkk-1 is secreted by mouse and human platelets in response to candidalysin and is required for robust allergic airway disease and C. albicans clearance from lung.
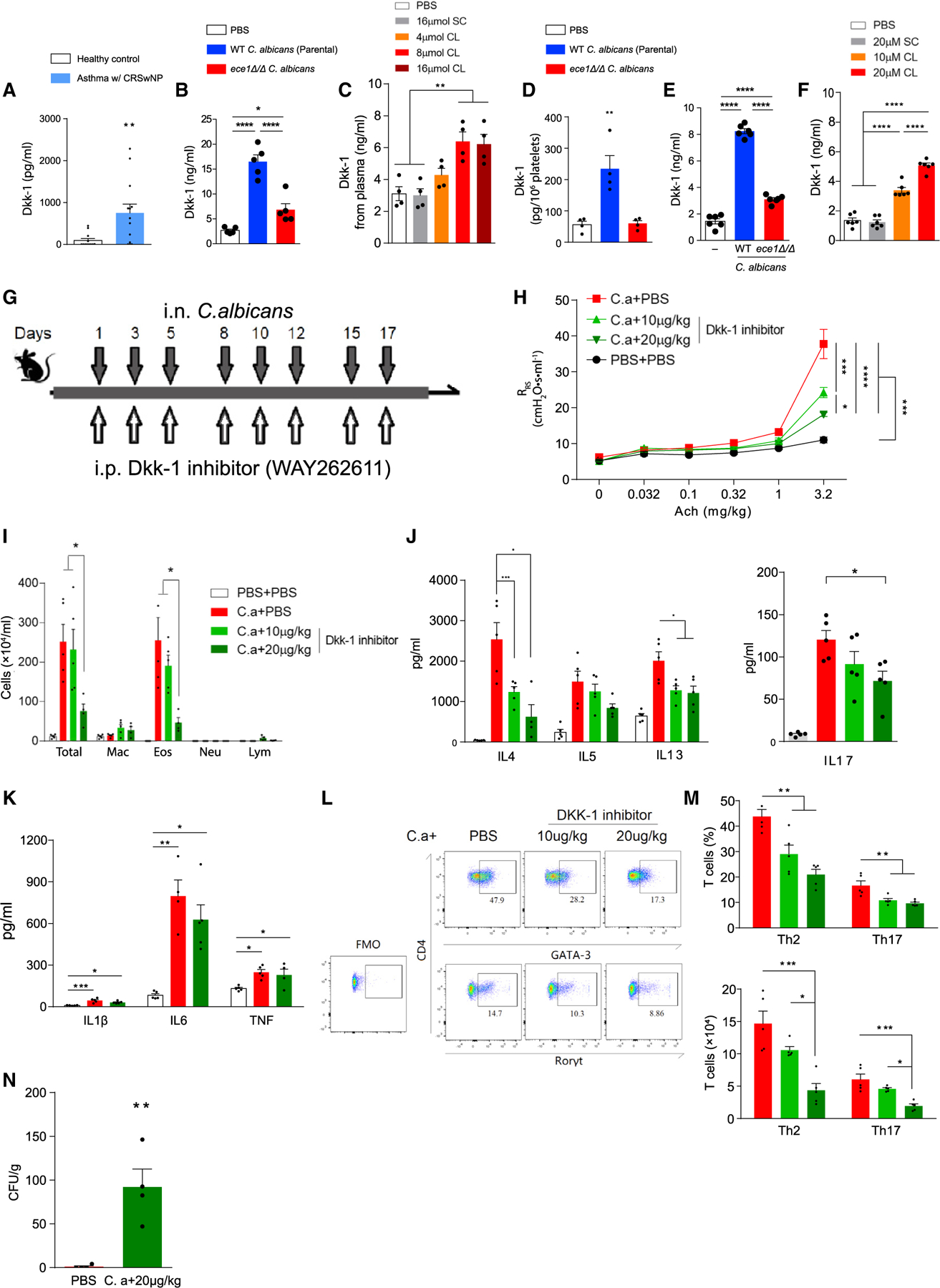
(A) Plasma Dkk-1 concentrations from patients with asthma and CRS as compared with non-allergic healthy controls.
(B and C) Dkk-1 concentrations quantitated from plasma of mice challenged intranasally with (B) wild-type parental strain or ece1Δ/Δ C. albicans or (C) candidalysin (CL) or scrambled control (SC).
(D) Dkk-1 was quantitated from platelets of mice challenged intranasally with wild-type or ece1Δ/Δ C. albicans.
(E and F) Human platelets in plasma were incubated with either (E) C. albicans or (F) CL/SC after which secreted Dkk-1 was quantitated.
(G) C57BL/6 mice were challenged intranasally with C. albicans (C.a) and intraperitoneally with Dkk-1 inhibitor (WAY262611) as shown.
(H) Respiratory system resistance (RRS) was quantitated as in Figure 1.
(I) Quantitation of cells from the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (mac, macrophages; eos, eosinophils; neu, neutrophils; lym, lymphocytes).
(J and K) Cytokines assessed by ELISA from lung homogenate supernatants including (J) IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, and IL-17 and (K) IL-1b, IL-6, and TNF.
(L and M) T cell quantitation from lungs as determined by flow cytometry. (L) Gating strategy for quantitation of Th1, Th2 and Th17 cells from lungs. (M) Quantitation of T cells assessed as percentages and absolute cell counts.
(N) Lung fungal burdens.
n ≥ 4, mean ± SEM. n.s., not significant; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, using Mann-Whitney test (A), one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons (B–M) or two-tailed Student’s t test (N). Data are representative of two independent experiments. See also Figure S3.
