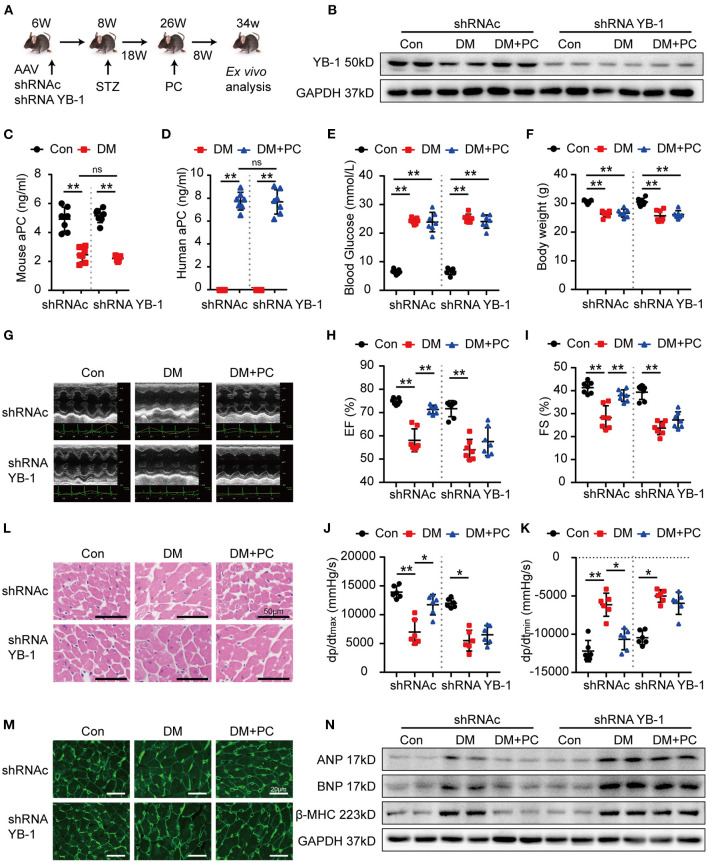
Figure 2.
Protection of PC in DCM depends on YB-1. (A) Schematic diagram of animal experiment. C57/BL6J mice were first administrated with YB-1 shRNA AAV9 or scrambled shRNA AAV9 via tail vein at the age of 6 weeks, following with STZ injection and PC intervention at indicated time points. (B) Representative YB-1 immunoblots of mice heart tissue lysates verifying the knock down effect of YB-1 shRNA. (C) Plasma endogenous mouse aPC level and (D) exogenous human PC activation in indicated experimental groups were detected by commercially available ELISA kits. (E) Random blood glucose was detected among the experimental groups. (F) Body weight was measured at the age of 34 weeks. (G) Echocardiographic images of left ventricle and (H,I) scatter plots summarized ejection fraction and fraction shorting results. (J,K) Scatter plots summarized the hemodynamic parameters, which were measured by Millar cardiac catheter system. (L) Exemplary images of H&E-stained heart section. Scale bar: 50 μm. (M) Exemplary images of WGA-stained heart section. Scale bar: 20 μm. (N) Western blots showed the expression levels of ANP, BNP, β-MHC in heart tissue from different animal groups. Data were presented as mean ± SD, (C–F,H,I) n = 7 for all groups; (J,K) n = 6 for all groups. Con, control; DM, diabetes mellitus; DM + PC, diabetes mellitus with PC treatment; shRNAc, scrambled non-specific shRNA; shRNA YB-1, YB-1 specific shRNA; EF, ejection fraction; FS, fraction shorting. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. Student's t-test or two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni comparison test. ns, no significance.