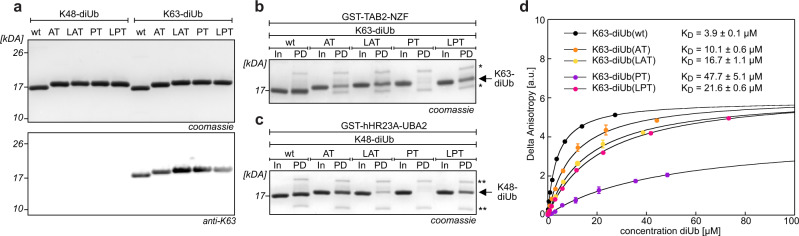
Fig. 2. Functional characterization of sortase-generated diUb building blocks used for Ubl-tools.
a SDS-PAGE of K48- and K63-linked diUbs displaying different sortase motifs at their linkage sites (top: Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gels, bottom: western blot (WB) using an anti-K63-linkage-specific antibody). b SDS-PAGE analysis of pull-down (PD) experiments using differently linked K63-diUbs and GST-fused TAB2-NZF. Single asterisk (*) marks impurities present in GST-TAB2-NZF. c SDS-PAGE analysis of PD experiments using differently linked K48-diUbs and GST-fused hHR23A-UBA2 (bottom). Double asterisks (**) marks impurities present in GST- hHR23A-UBA2. In: input of differently linked K48- or K63-diUbs, PD: pull-down. Full gels can be found in Supplementary Fig. 4. d Determination of binding constants of differently linked K63-diUbs towards fluorescently labeled Rap80-tUIMs(79–124) using fluorescence anisotropy. Delta anisotropy was plotted against diUb concentration and fitted with a single-site binding model to determine KD values. Average values and error bars (s.d.) were calculated from three different experiments (n = 3). All data processing was performed using Kaleidagraph software (Synergy Software, Reading, UK) or Prism 9.2.0 (GraphPad Software, LLC). Consistent results were obtained over at least three replicate experiments. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.