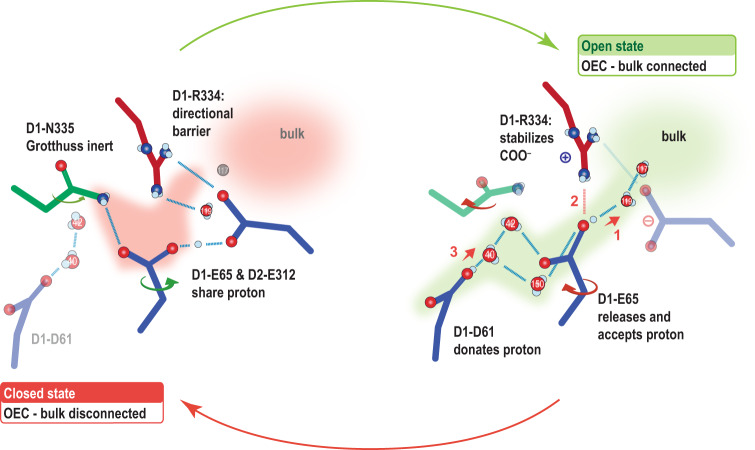
Fig. 6. The proposed proton gate around D1-E65, D2-E312, and D1-R334 in the open and closed state.
In the closed state, the H-bonding network connecting the OEC to the bulk is disrupted by D1-N335 and D1-R334, while in the open state, the OEC is connected via D1-E65 and waters to the bulk. The opening of the gate by the rotation of D1-E65 could be caused by the protonation of D1-D61 and the subsequent rearrangement of the H-bonding network. We hypothesized that the proton released towards the bulk was shared between the D1-E65 and D2-E312 before. The deprotonated D1-E65 can then be stabilized by approaching D1-R334. Rotation of D1-E65 back to the original position and closing of the gate may be caused by proton transfer from D1-D61 to D1-E65 and the subsequent repulsion and attraction of the newly arrived proton by D1-R334 and D2-E312, respectively.