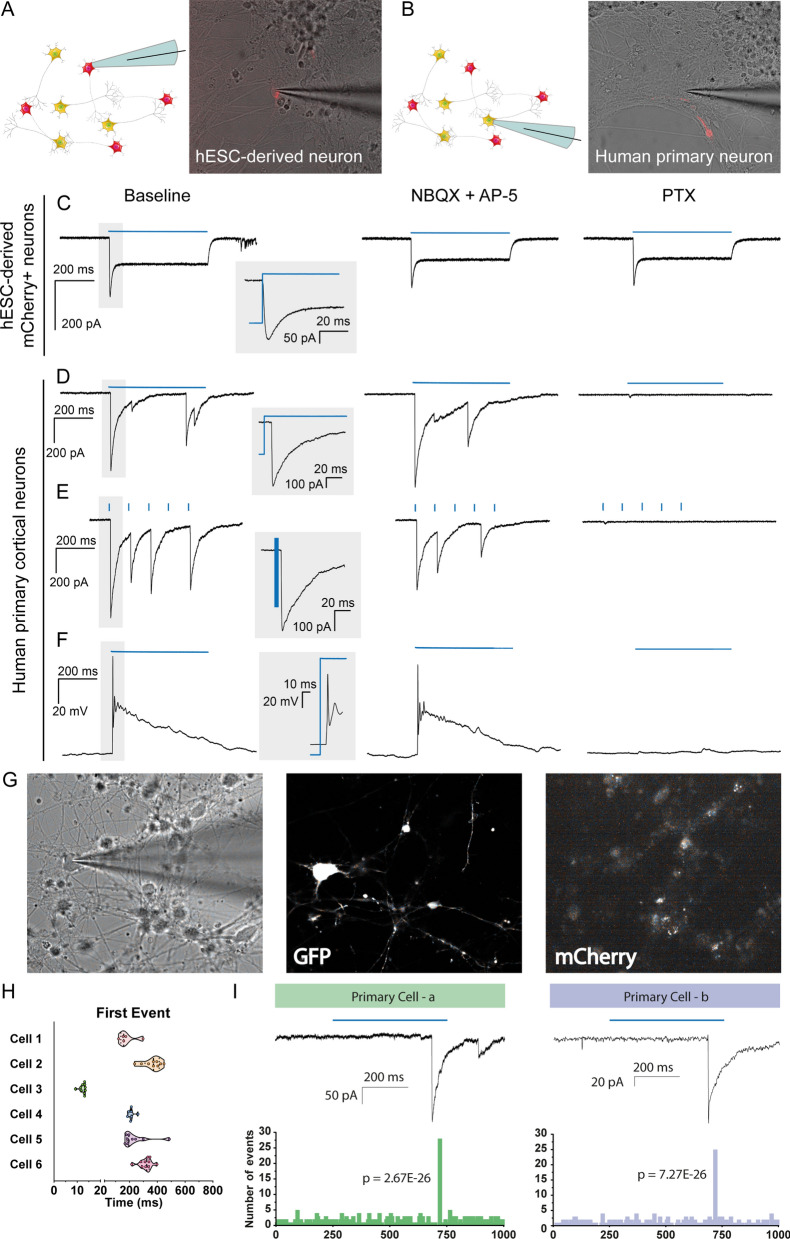
Figure 6.
Effect of ChR2 activation on the human primary neurons co-cultured with hdINs at 35 DIV. hdINs were co-cultured at 7 DIV with primary neurons from an 8-week-old human fetus for 4 weeks. Both (A) hdINs, expressing mCherry as a reporter for ChR2, and (B) human primary neurons were recorded (n = 18 and n = 6, respectively). (C) The activation of ChR2 by blue light in hdINs triggered an inward current, unaffected by either NBQX + AP5 or PTX. (D–F) Light activation of ChR2 in hdINs also generated a delayed synaptic response in the surrounding primary neurons, indicating synaptic integration of those cells in the pre-existing neuronal network. Light responses were assessed during (D) 500 ms light pulse in voltage-clamp, (E) light train of 5 pulses of 3 ms with 97 ms of interval between pulses in voltage-clamp, and (F) 500 ms light pulse in current-clamp. These responses in the primary cells were blocked by PTX (right column, D–F), but not by NBQX + AP5 (middle column, D–F), confirming their GABAergic nature. Note that the GABAergic currents are depolarizing in the primary neurons recorded because a high chloride internal solution was used in the patch pipette. (G) On the left, bright-field image of a primary neuron being recorded. In the middle, same cell showing GFP + expression. On the right, the primary neuron is mCherry- (negative). (H) Histogram of latencies of synaptic responses for each neuron recorded. Only the first event for each trace is included in the analysis. (I) Two examples of primary cells displaying delayed light-induced synaptic responses. On the top, traces in voltage clamp showing the synaptic responses to blue light stimulation (blue line) and, on the bottom, histogram of latencies of increased frequency of synaptic responses for each neuron recorded. P-value for Poisson test is indicated for the highest frequency distribution time. Blue line, light stimulation. Schematics were generated and adapted using resources from Servier Medical Art35.