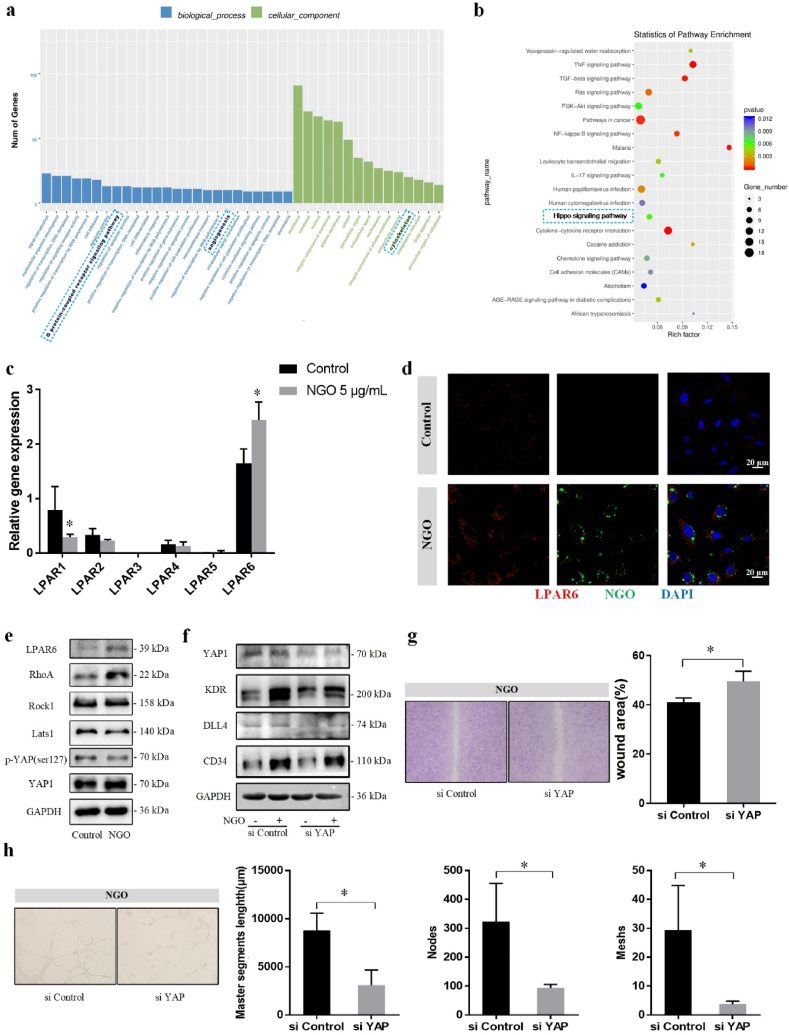
Fig. 6.
NGO activates endothelial tip cells via the LPAR6-Hippo-YAP signalling pathway. (a) Gene ontology analysis revealed the enrichment of biological processes, such as cell differentiation, angiogenesis and GPCRs, and cellular components involving the cytoskeleton. (b) The Hippo signalling pathway was enriched in the differentially expressed genes according to KEGG analysis. (c) The mRNA expression levels of LPAR1-6 in HUVECs treated with 0 or 5 μg/mL NGO for 24 h in RNA-seq detection. (d) Laser confocal microscopy showing that LPAR6 expression was upregulated in areas containing BSA-FITC labelled NGO. Scale bar, 20 μm. (e) Protein levels of LPAR6, RhoA, ROCK1, Lats1, p-YAP Ser127 and YAP1 in HUVECs treated with 0 or 5 μg/mL for 24 h were measured by western blotting. (f) Treatment with siRNA targeting YAP (200 nM) caused downregulation of the protein levels of KDR, DLL4, and CD34. (g) Wound healing assay of HUVECs treated with or without siYAP for 24 h in the NGO group. The wound area (%) was measured using ImageJ. (h) A tube formation assay was performed with HUVECs treated with siControl or siYAP and stimulated with NGO for 24 h. Quantitative analysis of the master segment length (μm) and numbers of nodes and meshes in the endothelial network. Data represent the mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05.