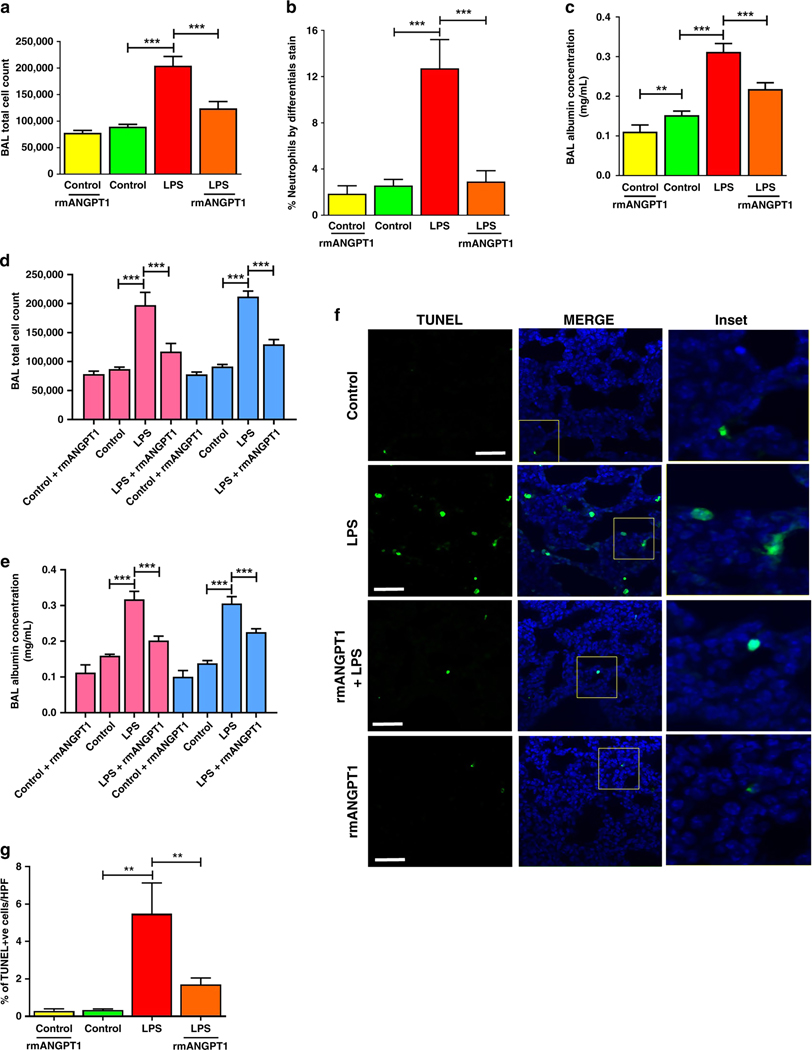
Figure 4– Acute lung injury is attenuated by rmANGPT1 in LPS-treated mice.
(A-C) Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) was performed on 11-day-old mice 24h after treatments with LPS (2mg/kg i.p) and 2h rmANGPT1 pre-treatment. Lavage fluid was used for: Total cell counts (A); Neutrophil quantification (B); Protein concentration (C) with quantifications shown graphically. (n≥5/condition, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 between Control and LPS; LPS and LPS+rmANGPT1; Control and Control+rmANGPT1.) (D-E) BAL total cell counts and albumin concentrations were analyzed by sex. Pink bars represent females and blue bars represent males. (n≥3/condition, ***p<0.001 between Control and LPS; LPS and LPS+rmANGPT1.) (F) 7-day-old mice treated with LPS, with or without rmANGPT1, were used to obtain lung tissue sections for TUNEL (green) and DAPI (blue) immunofluorescence. Scale bar indicates 50μm. (G) Graphical representation summarizing the ratio of TUNEL+ to total cell count per HPF. (n=5/condition, **p<0.01 between Control and LPS; LPS and LPS+rmANGPT1.) ANOVA (post-hoc Tukey) or Mann Whitney tests were used.