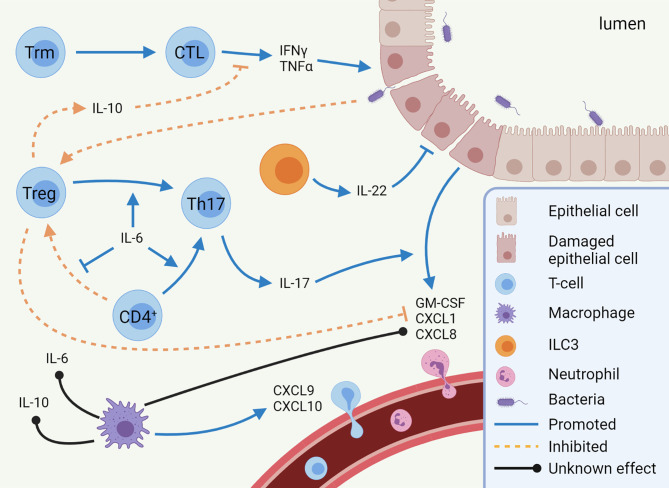
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of immune checkpoint inhibitor-mediated colitis (IMC). Pro-inflammatory pathways (CTL, Th17 cells, and neutrophils) are predominantly enhanced in IMC, while anti-inflammatory pathways (Treg differentiation and IL-10 secretion) are inhibited. Other cell types, such as macrophages and ILC3s, are expected to play a role in IMC, but to which extent is unknown. This image was created with BioRender.com. CTL, Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte; CXCL, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand; GM-CSF, Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IFN, Interferon; IL, Interleukin; ILC, innate lymphoid cell; Th17, T helper 17 cell; TNF, Tumor necrosis factor; Treg, regulatory T-cell; Trm, tissue-resident memory T-cell.