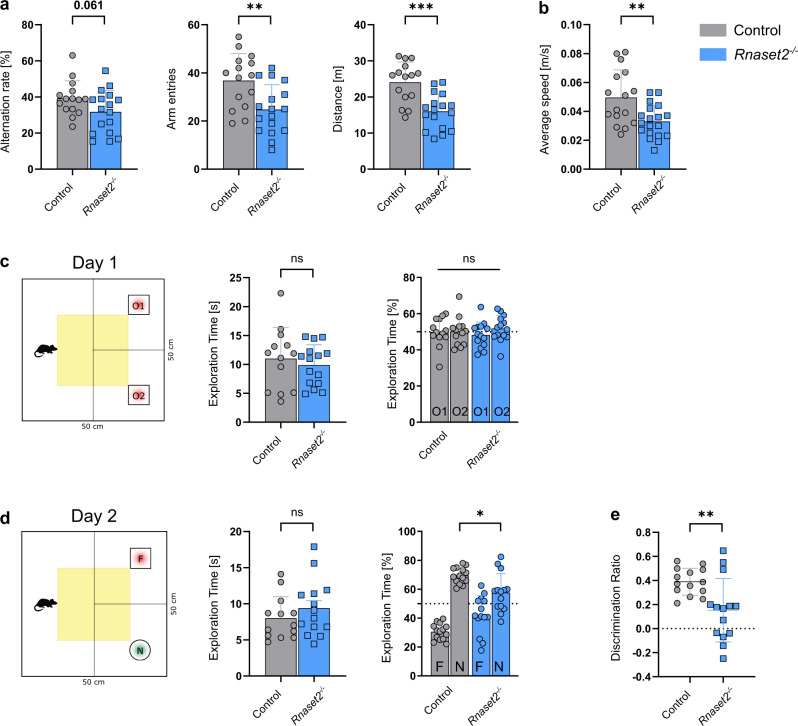
Fig. 6. Memory impairment in 4-month-old Rnaset2−/− mice.
a Cross maze testing: Percentage of spontaneous alternation (p = 0.061), total arm entries, and the average distance in meters of Rnaset2−/− (blue) and control mice (gray). Rnaset2−/− mice showed less activity, documented by a reduced number of arm entries (p = 0.0034) combined with a significant decrease of the average distance (p = 0.0001) covered in the cross maze. b Graph depicting the significantly reduced average speed of Rnaset2−/− compared to control mice in the open field box (p = 0.0031). c Novel object recognition (NOR) analysis in an open field box. Mean percentage of time spent exploring two similar objects (O1 and O2, red) and total exploration time on training day (Day 1) were similar in both genotypes. d Mean percentage of time spent exploring two different objects, the familiar (F, red) and a novel one (N, green), on testing day (Day 2) of the NOR test was significantly different between Rnaset2−/− mice and controls (p = 0.0456). e Discrimination ratio of Rnaset2−/− mice was significantly diminished (p = 0.0046). Rnaset2−/− n = 17, control n = 15. Values are given as the mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed with unpaired t-test and with two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey´s multiple comparison test. p values are represented as ****p < 0.0001, ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 and not significant (ns) p ≥ 0.05. Source data are provided as a Source data file.