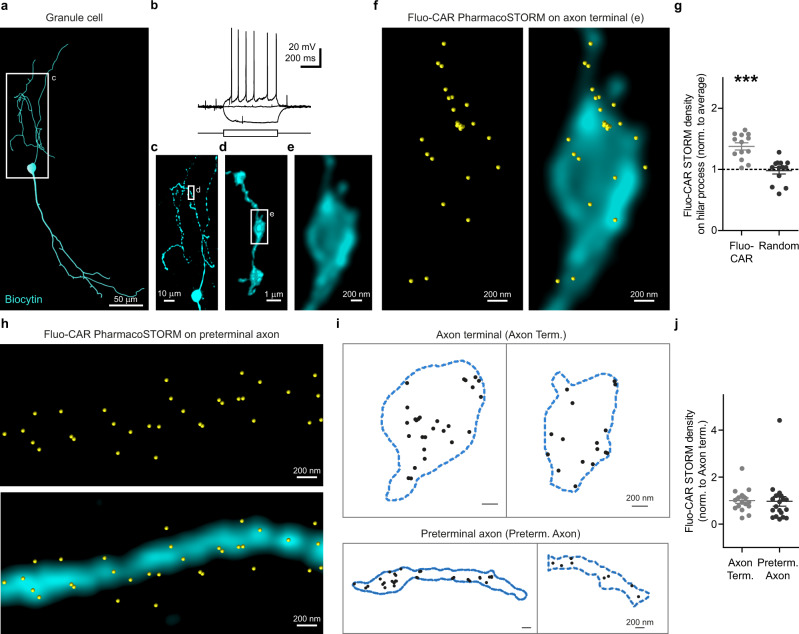
Fig. 7. Cell-type- and subcellular compartment-specific nanoscale distribution of fluo-cariprazine binding on the axons of the granule cells in the Islands of Calleja.
a–f Combination of nanoscale molecular imaging of Fluo-CAR-binding sites with cellular anatomical and electrophysiological characterization. a Neurolucida reconstruction of a representative biocytin-filled granule cell in the Islands of Calleja. b Voltage traces in response to +7 pA, 0 pA, −10 pA current steps from resting membrane potential recorded in whole-cell current-clamp configuration reveal the action potential firing pattern of the same granule cell shown in (a). c Maximum intensity z-projection of the confocal image stack of the hilar process in the boxed area in (a). d Volume view of a high-resolution confocal image stack taken from a varicose segment from boxed area in (c). e Higher magnification deconvolved confocal image of the boxed area in (d) illustrates a single axon terminal of the granule cell. f Correlated confocal and PharmacoSTORM imaging of the granule cell bouton (cyan) presented in (e), and the corresponding Fluo-CAR-binding sites (yellow) along the surface of the axon terminal. g Scatter dot plot shows the LP density on granule cell axons normalized to the average LP density on the same image. Two-tailed Wilcoxon signed-rank test shows that Fluo-CAR density on the axon of biocytin-filled cells is significantly higher than expected from random distribution (n = 13, n = 6 animals, P = 0.0002; P = 0.8394 for randomly distributed LPs). h Correlated confocal and PharmacoSTORM image of Fluo-CAR binding sites (yellow) on a long preterminal segment of a granule cell axon (cyan). i Schematic illustration of representative segmented PharmacoSTORM images for further analysis. Contours of axon terminals and preterminal axon segments are shown as blue dashed lines. Fluo-CAR LPs are represented as black dots. j Comparative analysis of nanoscale Fluo-CAR-binding site density on the distinct axonal subcompartments. Values are normalized to the mean density on axon terminals. Two-tailed Mann–Whitney test revealed no significant difference of Fluo-CAR-binding site density between the two subcellular compartments (axon terminals: n = 17, preterminal axon segments: n = 20, P = 0.402).