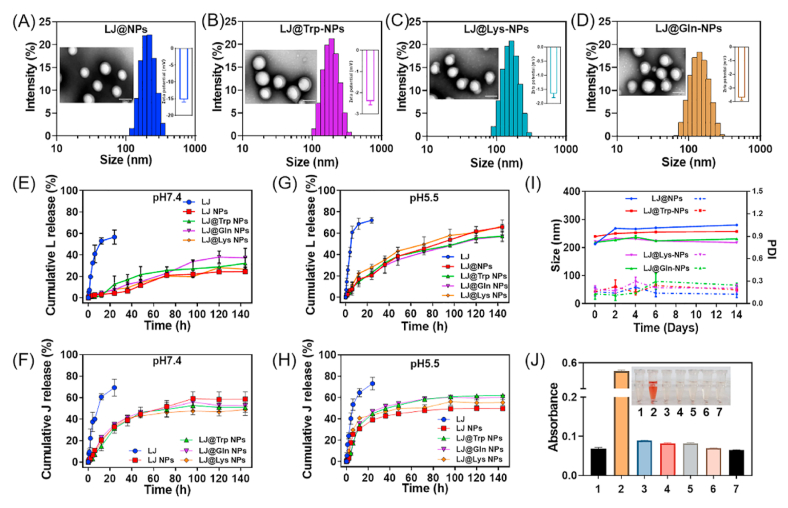
Fig. 2.
Characterization of lapatinib/JPH203-coloaded amino acid-targeted NPs. The size distribution, TEM image (Scale bar = 100 nm) and zeta potential of (A) LJ@-NPs, (B) LJ@Trp-NPs, (C) LJ@Lys-NPs, and (D) LJ@Gln-NPs. The cumulative release of (E) Lapatinib (L) or (F) JPH203 (J) from free LJ, LJ@NP, LJ@Trp-NP, LJ@Gln-NP, LJ@Lys-NP in pH 7.4 PBS at 37 °C. The cumulative release of (G) Lapatinib (L) or (H) JPH203 (J) from free LJ, LJ@NP, LJ@Trp-NP, LJ@Gln-NP, LJ@Lys-NP in pH 5.5 PBS at 37 °C. (I) The stability of LJ@NP, LJ@Trp-NP, LJ@Gln-NP, LJ@Lys-NP was indicated by the changes of particle size and polydispersity index (PDI) in pH 7.4 PBS at 37 °C. (J) The absorbance of the supernatant after incubation of blood cells with the following formulations: 1. saline, 2. 0.09% NaCl solution, 3. blank NP, 4. LJ@NP, 5. LJ@Lys-NP, 6. LJ@Trp-NP, and 7. LJ@Gln-NP. The results were presented as mean ± SD (n = 3).