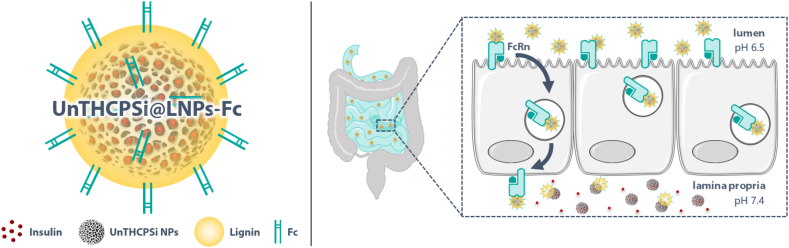
Scheme 1.
Schematic illustration of the multistage NP system designed in this study as a potential candidate for the administration of anti-diabetic drugs via the oral route. The nanosystem consists of an insulin-loaded porous silicon NP encapsulated into a pH-responsive lignin matrix (LNPs). The surface of these pH-sensitive NPs was further surface-functionalized with the Fc fragment of IgG. When reaching the intestinal cells, Fc-functionalized NPs would hijack the FcRn-mediated transcytotic pathway, being transported across the cells, and releasing the drug in the basolateral compartment, allowing them to reach blood circulation. Image created using Servier Medical Art (Creative Commons - Attribution 3.0 Unported - CC BY 3.0).