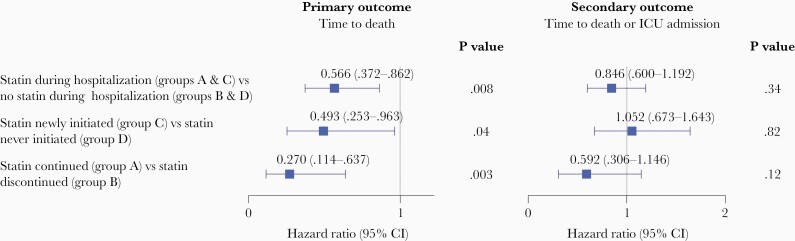
Figure 2.
Marginal structural model outputs for primary and secondary outcomes. Estimates were obtained from fitting marginal structural Cox models adjusted for the following baseline covariates: sex, age >65 years, race, active smoker, body mass index ≥30 (calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared), comorbid conditions on admission (coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, chronic liver disease, active cancer, pulmonary disease), angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor use, number of days since 1 March 2020, and prior statin usage. The following time–varying covariates were also adjusted for: absolute lymphocyte count, white blood cell count, aspartate aminotransferase, C-reactive protein, creatine kinase, alanine aminotransferase, and intensive care unit (ICU) admission status. Models were fit accounting for immortal time bias, time–varying confounding, and discharge as a competing risk. Applying a Benjamini-Hochberg correction to the primary outcome analysis, the 3 calculated P values all fall below the corrected significance thresholds: .003<.017, .008<.033, and .038<.05. Hazard ratios are given with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).