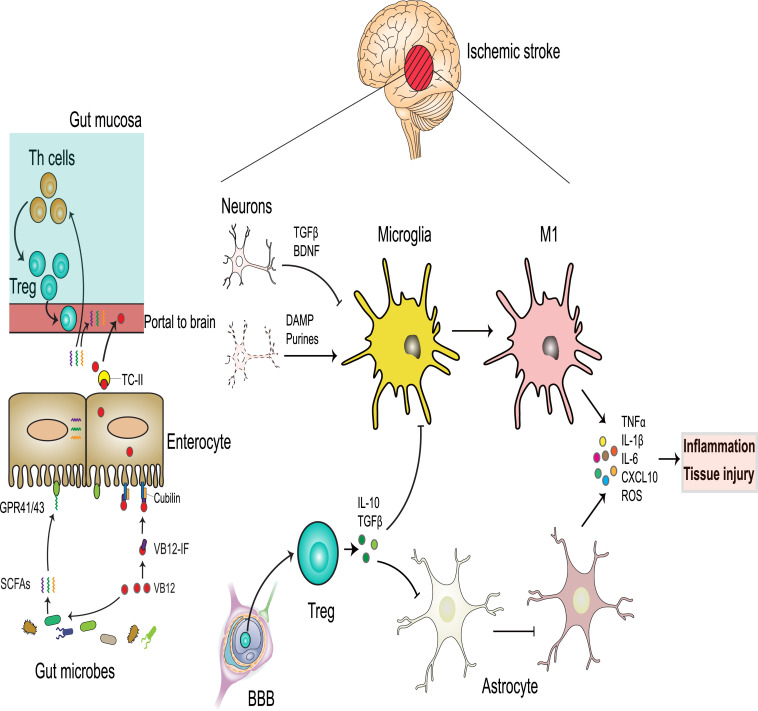
Fig. 2.
VB12 absorption and impact on neuroinflammation after ischemic stroke.
Gut microbes compete with IF for dietary VB12. VB12 promotes growth of SCFA-producing bacteria. SCFAs bind GPR41/43 in the intestinal epithelium and promote differentiation of naïve Th cells to functional FoxP3+ Tregs in the intestinal submucosa. Peripheral circulating immune cells are recruited to the brain parenchyma by crossing the disrupted BBB. Centrally-recruited Helios+ Tregs suppress highly activated astrocytes and microglia, which produce tissue injury and exacerbation of the inflammatory cascade by secreting inflammatory cytokines and injurious ROS. By contrast, dysfunctional Tregs lack the regulation of overactivated microglia with proinflammatory M1 phenotype and astrocytes, all of which further exacerbate toxic inflammation, potentially resulting in scar formation and tissue injury.