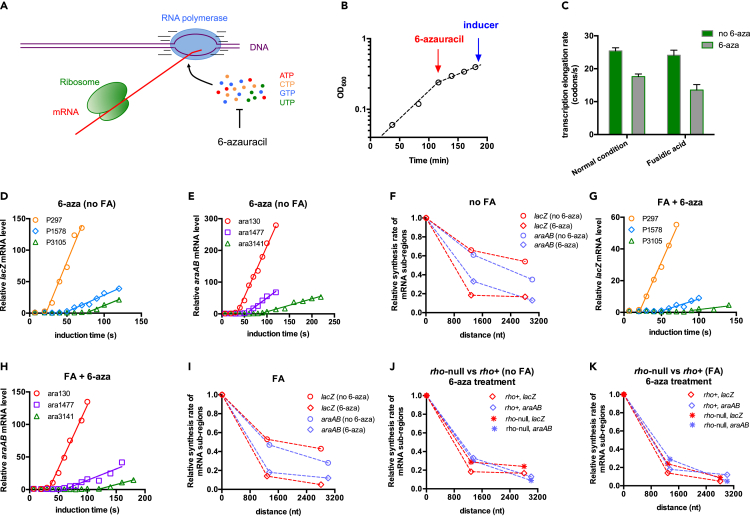
Figure 5.
Transcription kinetics of B. subtilis treated with 6-azauracil (6-aza)
B. subtilis cells were grown in gly + cAA medium.
(A) 6-Aza was used to perturb the transcription elongation process of B. subtilis through depleting the cellular nucleotides pools.
(B) The growth of B. subtilis treated with 6-aza. Cells were first exponentially grown in gly + cAA medium to OD600∼0.25. 6-Aza, 500 μg/mL, was then added to deplete the cellular nucleotides pools. The cell culture was further incubated for 1 h before measuring transcription kinetics.
(C) The effect of 6-aza on the transcription elongation rate of B. subtilis. Cells were grown in gly + cAA medium supplemented with/without 0.2 μg/mL FA. Data are represented as mean ± SD.
(D) and (E) The induction kinetics of lacZ mRNA and araAB mRNA in B. subtilis treated with 6-aza. FA was not supplemented in this case.
(F) Comparison of the transcription processivities of lacZ (red) and araAB (light purple) mRNA in B. subtilis (rho+ strain) with (diamond)/without (circle) 6-aza treatment. FA was not supplemented in this case.
(G) and (H) The induction kinetics of lacZ mRNA and araAB mRNA in B. subtilis treated with 6-aza. Being different from D and E, cells were grown with 0.2 μg/mL FA. The growth curve is shown in Figure S12.
(I) Comparison of the transcription processivities of lacZ (red) and araAB (light purple) mRNA in B. subtilis (rho+ strain) with (diamond)/without (circle) 6-aza treatment. Cells were grown with 0.2 μg/mL FA.
(J) and (K) Comparison of the transcription processivities of rho+ strain and rho-null strain during 6-aza treatment.