Figure 3: (A).
Overall structure of the human Pol ƞ-DNA ternary complex in the presence of the 5fC-conjugated to the 11-mer peptide with incorrect incoming dATP at the insertion site. Inset box: the DNA sequences are indicated. See Movie S1.
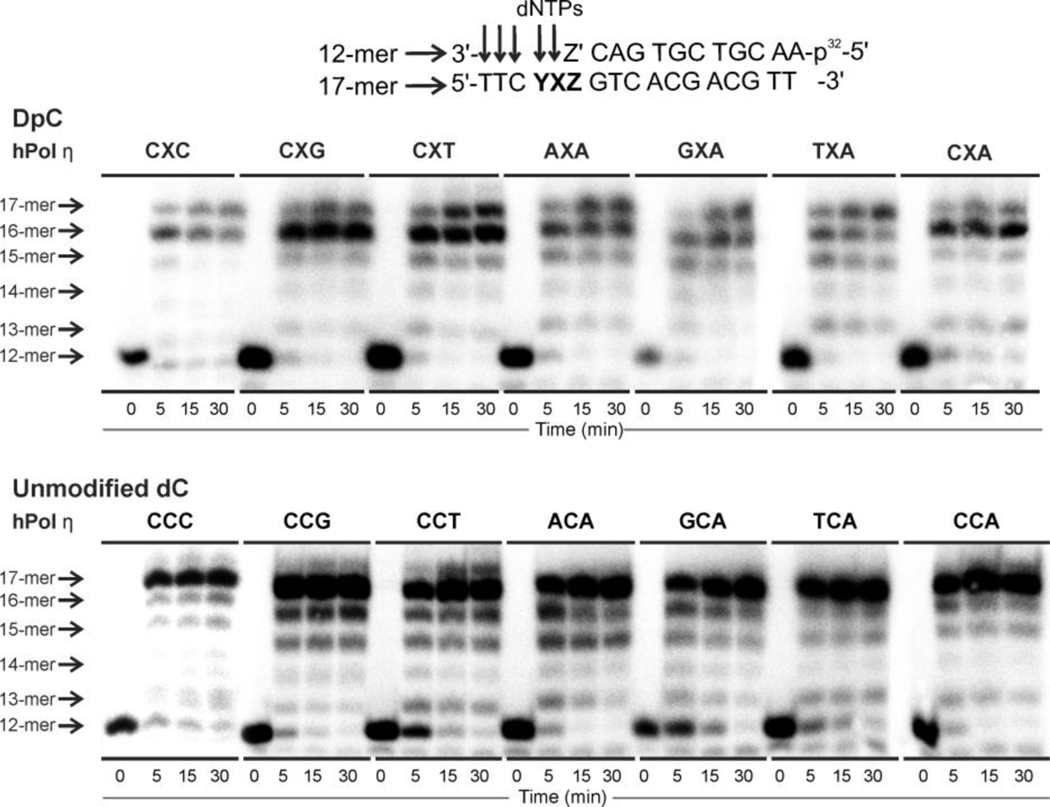
(B) In the local sequence YXZ, Y is the unpaired nucleotide on the 5’-side to the template base; Z, on the 3’-side to the template base, forms a Watson-Crick base pair with Z’ at the primer terminus; X is the modified template 5fC with its major-groove C5 atom conjugated to the oxy-lysine (K*) via a −C=N− linker. In oxy-lysine, the ɛ-CH2 group was replaced with an oxygen atom. The incoming dATP forms a C─A mismatched base pair with template 5fC-conjugated to the 11mer-peptide. The C─A mismatch is modeled with a two-hydrogen bond scheme as a C─A wobble pair (inset box).
(C) The effects of the neighbor sequences to the template base on the alignments of the C─A mismatch. The effect of the base-pair on the 3’-side of the template base: a slipped H-bond between the template base and the primer terminus can form to distort the alignment of the C-A mismatch. The effect of the unpaired nucleotide on the 5’-side of the template base: the thymine with its small size and methyl group fits well and stably into a pocket in the finger domain via hydrophobic interactions; it therefore stacks well with the template base which stabilizes the alignment of the C-A mismatch.
(D) The effect of the major-groove-positioned DpC: Superimposed are the structures of CCG (grey) and CXG (red) sequences, showing that the peptide, which is housed in the major groove, pulls the template base toward the major groove and its 3’-side. The ability of the peptide to pull the template base is most restrained in the CXT sequence. This is because the 3’-thymine restrains the DpC (the close contact highlighted as blue surface) via hydrophobic interactions with its methyl group. Furthermore, this 3’-thymine methyl group stacks well with the C6 atom of the template base, and thus inhibits the template base from being pulled away by the DpC.