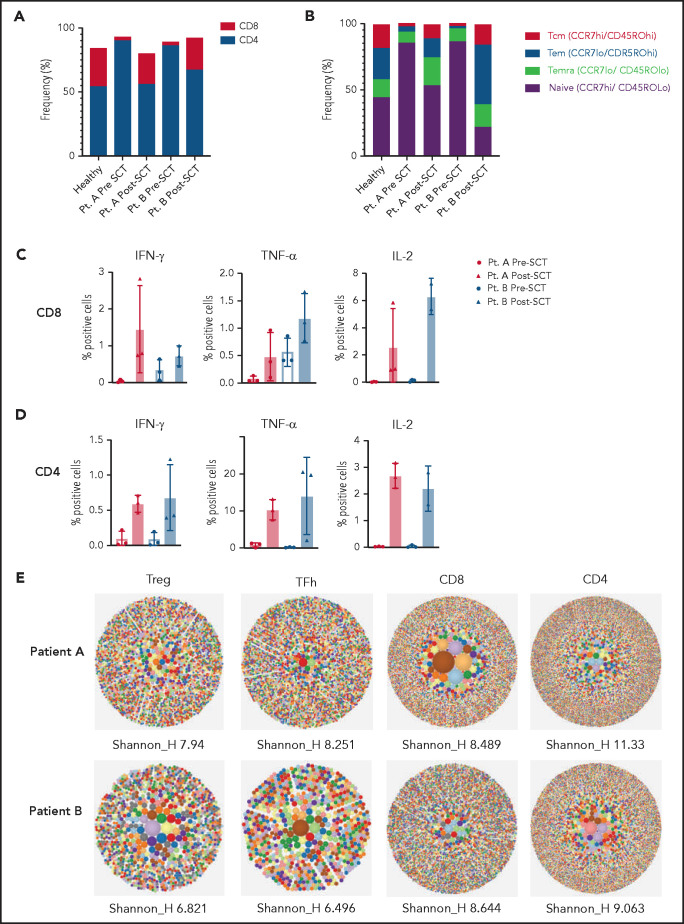
Figure 2.
T-cell compartments and T-cell cytokine production are restored after hematopoietic stem cell transplant. (A) T-cell subsets evaluated before transplant show a decreased proportion of CD8+ T cells and increased proportion of CD4+ T cells compared with control that increase and decrease, respectively, posttransplant to proportions that are comparable to control T cells. The figure is representative of 3 independent repeats pre- and posttransplant. (B) T-cell memory subsets before transplant show an increased proportion of naive T cells (CCR7hi/CD45ROLo) and a reduced proportion of effector and effector memory T cells (CCR7lo/CD45ROhi and CCR7lo/CD45ROlo). (C) Cytokine secretion (interferon-γ [IFN-γ], interleukin-2 [IL-2], and tumor necrosis factor-α [TNF-α]) in pre- and posttransplant CD8+ T cells. Graphs show percent of positive cells after staphylococcal enterotoxin B stimulation, normalized to control for each cytokine. Cells were gated on live cells, CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ T cells, and percentage of cytokine secreting cells was determined against side scatter for each subset. Cytokine secretion was measured on 3 separate time points before transplant and at least twice posttransplant. (D) Cytokine secretion in CD4+ T cells pre- and posttransplant. Graphs show percent of positive cells after staphylococcal enterotoxin B stimulation normalized to control for each cytokine. Cells were gated on live cells, CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ T cells, and percentage of cytokine-secreting cells was determined against side scatter for each subset. Cytokine secretion was measured on 3 separate timepoints before transplant and at least twice posttransplant. (E) TCRb repertoire was determined by high-throughput sequencing of sorted T-cell subsets (T conventional, CD8+ T cells, Treg, T follicular helper cells). Representative hierarchical tree maps show TRB repertoire diversity in patient PBMC samples after transplant. Each dot represents a unique CDR-3, and the size of each dot corresponds to the frequency of that CDR-3 in the total population of sequences obtained. Shannon’s H entropy index measures the diversity of the repertoire, taking into account the clonal size distribution in the overall repertoire, and is indicated below each tree map.