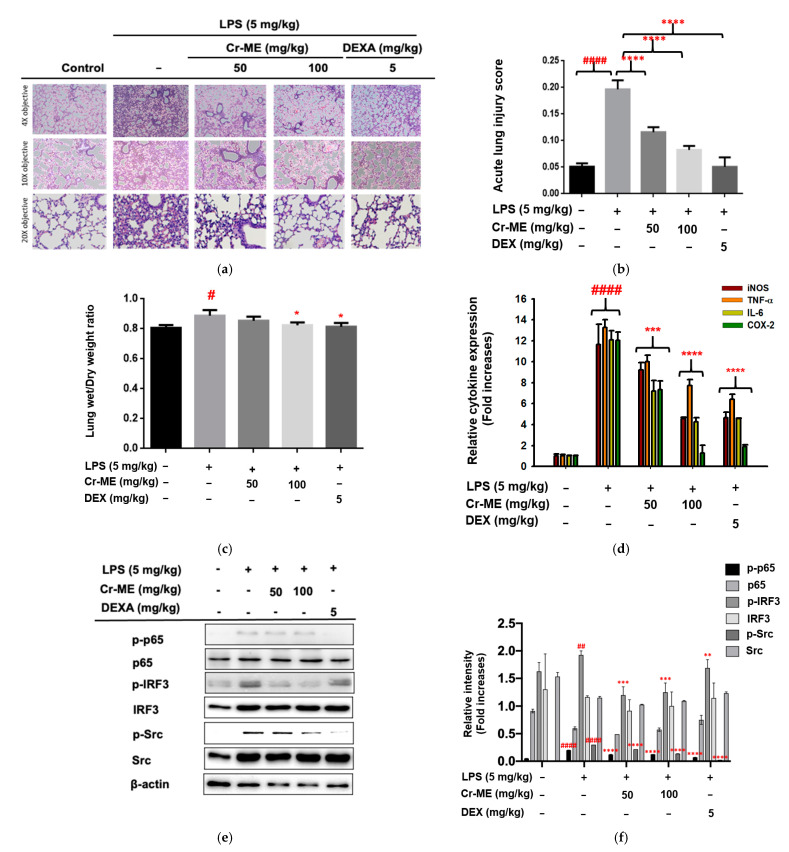
Figure 5.
Effect of Cr-ME treatment on LPS-induced acute lung injury (ALI). (a,b) Histological analysis was performed to visualize the inhibitory activity of Cr-ME in LPS-induced acute lung injury conditions of mice after 16 h of LPS instillation (a). H&E stain was applied to the sections, original magnification, 200×. Acute lung injury scores were calculated according to parameters indicated in Table 1 (b). (c) The effect of Cr-ME on pulmonary edema was determined by calculating the lung wet/dry weight ratio. (d) The mRNA expression levels of inflammatory genes were determined by real-time PCR. (e,f) The total and phospho-forms of p65, IRF3, Src, and β-actin were analyzed by Western blotting analysis performed with tissue lysates from the LPS-induced ALI mice (e). Relative intensity of these proteins was calculated by ImageJ (f). All the data (b–d,f) expressed as the mean ± SD of 7 mice or three independent experiments. Relative band intensity was measured using ImageJ Values are mean ± SD (n = 5 per group). Statistical significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA (Dunnett’s t-test). # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.001, and #### p < 0.0001 compared to normal group, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001 compared to LPS group.