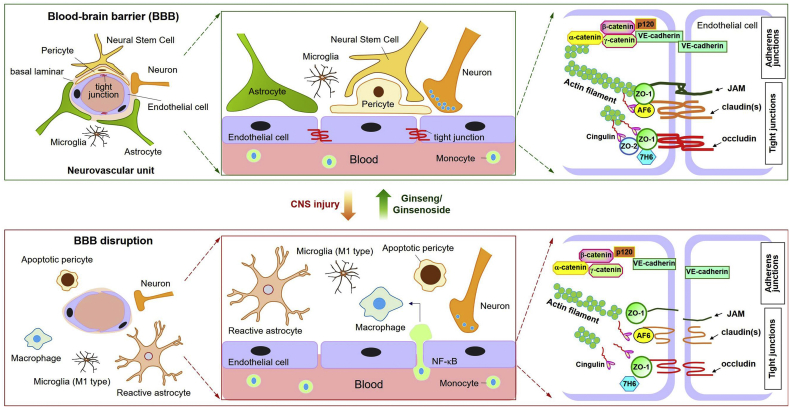
Fig. 2.
Blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity is maintained by ginseng/ginsenosides following central nervous system (CNS) injury. The neurovascular unit refers to functional coupling of brain endothelia with other local cells (e.g. pericytes, astrocytes, microglia, neural stem cells, and neurons) and the extracellular matrix. Endothelial tight junctions and integral proteins are involved in regulation of paracellular permeability. Following CNS injury, expression patterns - including site and level - of tight junction and integral proteins become altered. Damaged endothelia exhibit markedly increased NF-κB activation, leading to infiltration of monocytes into the brain parenchyma, where they become activated macrophages. Additionally, concomitant disruption of functional cellular associations is accompanied by breakdown of BBB integrity. Damaged brain parenchyma exhibits activated astrocytes and M1-polarized microglia, apoptotic pericytes, and neurotransmitter-degraded neurons. Abbreviations: JAM, junction adhesion molecule; ZO-1, zonula occluden-1; AF6, afadin 6; VE-cadherin, vascular endothelial cadherin; NF-κB, nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells.