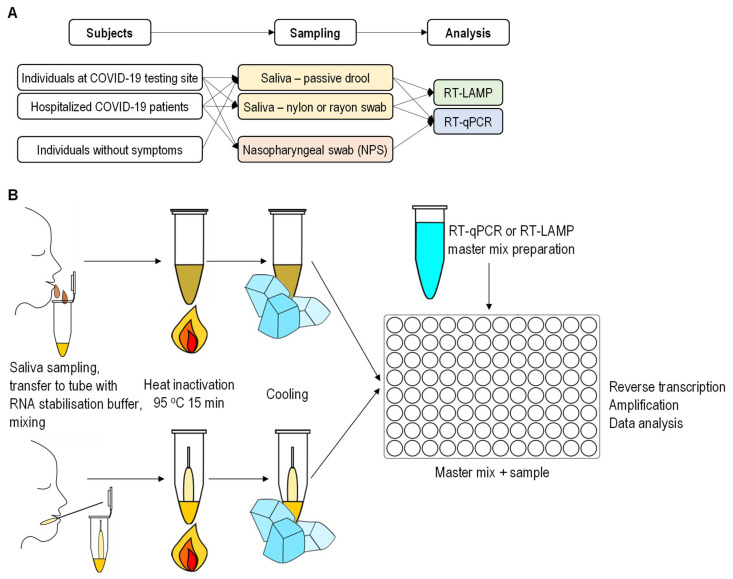
Figure 1.
Diagnostic workflow for SARS-CoV-2 testing in saliva specimens. (A) Design of the study. Samples were collected from three groups of individuals: (i) individuals with the risk of being infected, (ii) COVID-19 patients admitted to a hospital and (iii) individuals without symptoms. Three saliva-sampling techniques were compared: passive drool and oral cavity swabs with nylon- and rayon-tipped applicators. NPS-paired saliva specimens were collected from asymptomatic and symptomatic individuals at the COVID-19 testing site. The specimens were analyzed for SARS-CoV-2 with RNA extraction-free one-step RT-LAMP or RT-qPCR. The NPS specimens were analyzed at the official testing laboratory National Laboratory of Health, Environment, and Food with a diagnostic RT-qPCR test, including RNA extraction. (B) Workflow of SARS-CoV-2 testing. Saliva as (i) an oral cavity swab or (ii) passive drool was collected in a tube with an RNA stabilization buffer. The specimen was heat-treated. After cooling, a one-step RT-LAMP or RT-qPCR test was conducted to detect SARS-CoV-2 in the saliva.