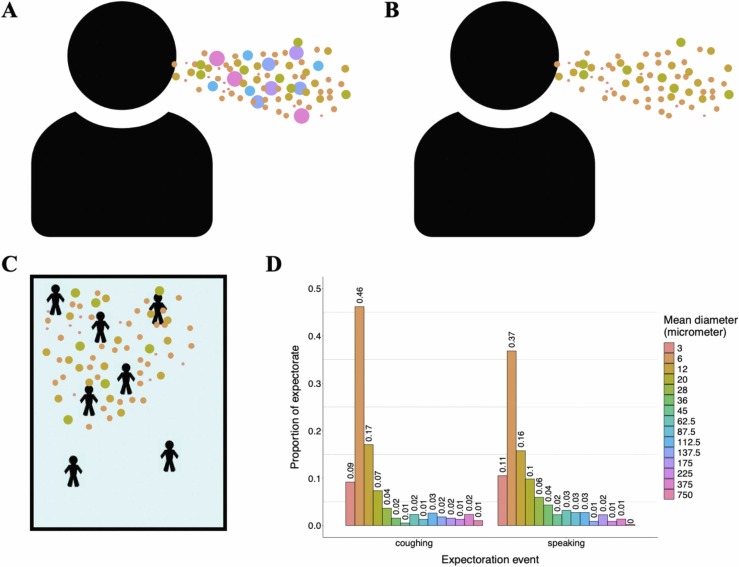
Fig. 1.
Model droplet dynamics. A) Infectious individuals expel droplets of different sizes. B) Relatively large droplets fall out of the air quickly post expectoration. C) Smaller droplets remain aerosolized for longer time periods and move throughout the simulated room via diffusion and forced airflow effects. D) Distribution of droplet sizes during expectoration events. Distributions of size classes during coughing and speaking events are based on findings of Chao et al. (2009), and represent mean observed droplet-size measurements they recorded 60 mm away from individuals’ mouths immediately following these activities.